There is now a lot of attention and focus on data. However, is the same applied to change management data? With the substantial financial investments companies make in change efforts, there’s a growing recognition of the need to leverage change management data strategically. Senior managers and executives are increasingly demanding data-driven insights to make informed business decisions. Here, we explore the challenges associated with change data, the strategic approaches to managing it effectively, and how incorporating it into the decision-making process can drive organizational success.
Common Challenges in Working with Change Data
- Ad hoc and Tactical Approaches
One common challenge in working with change data is the ad hoc and tactical nature of its collection. Often, data is gathered as needed, primarily at the project level. This can result in a fragmented view of change initiatives, making it challenging to derive meaningful insights. For instance, progress data may be limited to generic metrics such as the number of change impact sessions or completed training sessions, lacking depth and context. - Data Insufficiently Fact-Based
Another prevalent issue is the creation of data that lacks a solid factual foundation. Change practitioners sometimes rely on gut-feel ratings or broad categories that are difficult to defend or substantiate infront of stakeholders. Heatmaps, a popular visualization tool, may be based on subjective assessments rather than objective, quantifiable measures, hindering the data’s credibility and utility. - Ineffective Data Visualizations
Data visualizations play a crucial role in conveying information effectively. Unfortunately, some visualizations fall short of making a significant impact. Whether they are overly colorful, fail to use the right chart to highlight key points, or present data in a way that obscures the primary message, ineffective visualizations can impede the decision-making processes. - Seeking Easy Fixes
Many change practitioners view working with data as a chore and opt for quick fixes. They may collect just enough data to generate a report or dashboard, neglecting the importance of a thorough understanding and management of the data. This short-sighted approach can compromise the quality and reliability of the insights derived from the data.
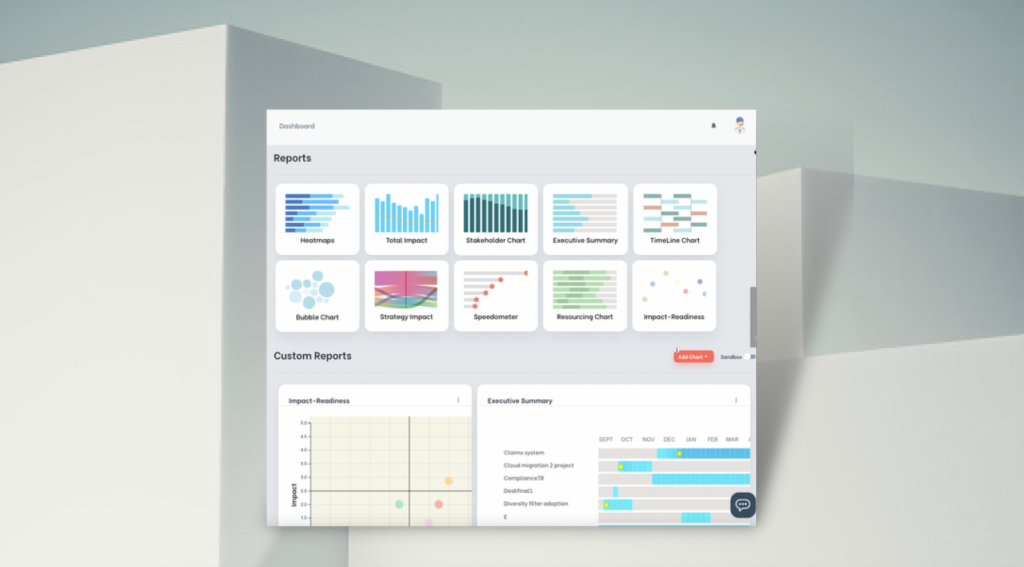
Strategic Approaches in Working with Change Data
Strategic approaches to manage change data can result in significant value for the organisation. Imagine the power of a range of change management data that highlights anything from impact levels, saturation risks, sentiments, adoption risks and benefit realization progress. Such is the power of change data, if managed effectively. What are some of these strategic approaches?
- Managing Data as a Core Routine
To address the challenges associated with ad hoc and tactical data collection, organizations must establish routines for managing change data. Monthly data reviews, updates, and audits create a disciplined approach to ensure the data remains accurate, relevant, and valuable. By making data management a core routine, organizations foster a culture of accountability and accuracy. This can be applied across a large program, a business unit, a portfolio of initiatives or across the enterprise. - Leveraging AI for Data Auditing and Cleansing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can play a pivotal role in auditing and cleansing change data. Platforms like The Change Compass offer features that automate these processes, reducing the likelihood of errors and ensuring data integrity. AI-driven tools can identify inconsistencies, outliers, and inaccuracies, providing a more reliable foundation for decision-making. - Linking Change Data with Other Business Sources
The true power of change data emerges when it is connected with other relevant business data sources. By integrating change management data with project data, HR data, risk data, and operations data, organizations gain a holistic view of their business landscape. This interconnected approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of key business risks and opportunities, facilitating more informed decision-making. - Incorporating Data into Decision-Making Bodies
Change data should not exist in isolation; it should be integrated into key decision-making forums and processes. From executive leadership forums and strategic planning sessions to portfolio planning and operational meetings, incorporating change data into these discussions ensures that insights derived from the data inform critical business decisions. This alignment helps organizations proactively address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.

While recognizing the strategic importance of change data is a significant step forward, change practitioners must actively implement practical measures to enhance their approach to change data management. Here are some recommendations to help change practitioners become more strategic in their utilization of change data:
- Standardize/Routinize Data Collection Processes:
o Develop standardized processes for collecting change data across different projects and initiatives.
o Implement consistent data collection templates and methodologies to ensure uniformity and comparability of data across initiatives and business units - Invest in Training and Skill Development:
o Provide training for change practitioners on data management best practices, including data collection, analysis, audit and interpretation. This is critical to drive data capability and maturity.
o Foster a data-driven culture within the organization by equipping practitioners with the necessary skills to leverage data effectively. - Utilize Technology and Automation:
o Embrace technological solutions, such as data analytics tools and AI-driven platforms, to automate data auditing, cleansing, and visualization processes.
o Leverage technology to streamline data collection and reporting, reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of errors. - Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration:
o Facilitate collaboration between change management teams and other departments, encouraging the sharing of data and insights.
o Establish cross-functional teams to integrate change data with project data, HR data, and other relevant business sources. - Implement Data Governance Frameworks:
o Develop and implement robust data governance frameworks to ensure the accuracy, security, and compliance of change data.
o Define roles and responsibilities for data management within change initiatives, promoting accountability and ownership. - Enhance Data Visualization and Reporting:
o Invest in training or hiring professionals with expertise in data visualization to create compelling and impactful reports.
o Tailor visualizations to the audience, ensuring that key messages are communicated clearly and effectively. - Conduct Regular Data Reviews and Audits:
o Establish a routine for regular data reviews, updates, and audits to maintain the accuracy and relevance of change data.
o Use audits as an opportunity to identify and rectify data discrepancies or inconsistencies. - Integrate Change Data into Decision-Making Processes:
o Actively participate in executive leadership forums, strategic planning sessions, and other decision-making bodies.
o Present change data alongside other relevant business data to contribute to well-informed decision-making. - Measure and Communicate Value:
o Develop metrics to measure the value generated by change initiatives and communicate these metrics to key stakeholders.
o Regularly assess the impact of change data on decision-making processes and adjust strategies accordingly. - Seek Continuous Improvement:
o Foster a culture of continuous improvement within the change management function.
o Encourage practitioners to reflect on past experiences, learn from challenges, and refine their approach to change data management over time.
The strategic management of change data is not just a necessity but a critical component of achieving business success in today’s dynamic environment. By addressing common challenges and adopting strategic approaches, organizations can unlock the true potential of change data. As the business landscape continues to evolve, leveraging data-driven insights becomes a strategic imperative for navigating change, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on opportunities. Embracing change data as a strategic exercise positions organizations to not only survive but thrive in an ever-changing marketplace.