Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) has emerged as a leading methodology to address organisational change demands of fostering flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. A cornerstone of SAFe is the principle of “Measure and Grow,” which emphasizes using data and fact-based decisions to enhance change outcomes over time. Despite its centrality, SAFe does not explicitly detail the change management components essential for its success. Here we outline how change management practitioners can effectively apply the “Measure and Grow” principle to lead change and improve outcomes to support the Scaled Agile environment.
The “Measure and Grow” Principle in Scaled Agile
“Measure and Grow” is integral to SAFe, focusing on systematic measurement and continuous improvement. By leveraging data and analytics, organizations can make informed decisions, identify areas needing attention, and iteratively enhance performance. For change management professionals, this principle translates into a structured approach to evaluate the effectiveness of change initiatives, pinpoint areas for improvement, and implement necessary adjustments.
In a Scaled Agile environment, “Measure and Grow” is a core tenant or principle that applies in all types of agile environments. By continuously assessing and refining change efforts, organizations can align their initiatives with strategic objectives, mitigate risks, and ensure sustained success.
In practice, a lot of organisations have not pinpointed exactly how change management measures can make or break the outcome of the change, and in a SAFe environment, across the program, portfolio as well as enterprise.
The ‘Measure and Grow’ principle as a core part of SAFe (From Scaled Agile Framework)

Key Elements of Measuring and Growing Change Outcomes
To operationalize the “Measure and Grow” principle in change management, it is crucial to establish a set of metrics and assessment frameworks. Here are some broad categories of different types of change measurements that are relevant. Note that since we are talking about SAFe, it is not just at the initiative level that we are talking about metrics. More importantly, it is about establishing a system to promote change improvement across the organisation.
Change Management KPIs and OKRs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are essential tools for tracking the success of change management initiatives. KPIs provide quantitative measures of performance, while OKRs align change efforts with broader organizational goals. A change management stream or function should focus on establishing KPIs or OKRs to achieve laser focus on achieving change outcomes.
Examples of Initiative-Level Change Management KPIs that may roll out to form portfolio views
- Employee Engagement Levels: This KPI assesses how change impacts employee morale and engagement, providing insight into the overall acceptance and support of the change initiative.
- Learning Achievement Rates: This can include tracking the percentage of employees who have completed necessary training programs, as well as achieving the target level of competence to ensure that the workforce is adequately prepared for the change.
- Feedback Scores: Collecting feedback from stakeholders through surveys or feedback forms helps gauge perception and identify areas needing improvement. It is important to note that depending on the change context, stakeholders may not be happy with the content of the change. However, understanding and tracking this perception is still important.
- Change Adoption Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of stakeholders who have adopted the change. High adoption rates are the ultimate goal for initiatives.
- Issue Resolution Time: Measuring the time taken to resolve user-related issues related to the change highlights the efficiency of support mechanisms and the responsiveness of the change management team. This is especially important during an agile environment where there may be constant changes.
Change Readiness and Stakeholder Engagement Metrics
Evaluating change readiness and stakeholder engagement is crucial to the success of any change initiative. These metrics help assess the organization’s preparedness for change and the level of involvement and support from key stakeholders. Readiness and engagement rates can also roll up at a portfolio level to provide oversight.
Change Readiness Metrics
- Readiness Assessments: Conduct surveys or interviews to gauge the organization’s preparedness for the impending change. This can include evaluating awareness, understanding, and acceptance of the change.
- Resource Availability: Measure the availability of necessary resources, such as budget, personnel, and tools, to support the change initiative.
- Communication Effectiveness: Assess the clarity, frequency, and effectiveness of communication regarding the change to ensure stakeholders are well-informed and engaged.
Stakeholder Engagement Metrics
- Engagement Scores: Use surveys or feedback forms to measure the engagement levels of stakeholders, indicating their commitment and support for the change.
- Participation Rates: Track stakeholder participation in change-related activities, such as workshops, meetings, and training sessions, to gauge their involvement.
- Influence and Support: Assess the influence and support of key stakeholders in driving the change, ensuring that influential figures are actively endorsing the initiative.
By monitoring these metrics, change management professionals can identify potential barriers to change and take proactive steps to enhance readiness and engagement.

Stakeholder Competency Assessment
Successful change initiatives rely on the competence and readiness of key stakeholders. Assessing stakeholder competency involves evaluating the capability of sponsors and change champions to support and drive the change.
Sponsor Readiness/Capability Assessment
- Sponsor Engagement: Measure the level of engagement and commitment from sponsors, ensuring they are actively involved and supportive of the change.
- Decision-Making Effectiveness: Assess the ability of sponsors to make timely and effective decisions that facilitate the change process.
- Resource Allocation: Evaluate the sponsor’s ability to allocate necessary resources, such as budget and personnel, to support the change initiative.
Change Champion Capability Assessment
- Training and Knowledge: Measure the knowledge and training levels of change champions to ensure they are well-equipped to support the change.
- Communication Skills: Assess the ability of change champions to effectively communicate the change message and address stakeholder concerns.
- Influence and Leadership: Evaluate the influence and leadership capabilities of change champions, ensuring they can effectively drive and sustain the change.
By conducting these assessments, change management professionals can ensure that key stakeholders are prepared and capable of supporting the change initiative.
Change Adoption Metrics
Change adoption metrics provide insight into how well the change has been accepted and integrated into the organization. These metrics help assess the effectiveness of the change initiative and identify areas for improvement. At a portfolio level, there may be different levels of change adoption set for different initiatives depending on priority and complexity.
Key Change Adoption Metrics
- Adoption Rate: Measure the percentage of stakeholders who have adopted the change, indicating the overall acceptance and integration of the new processes or systems.
- Usage Metrics: Track the usage of new tools, processes, or systems introduced by the change to ensure they are being utilized as intended.
- Performance Metrics: Assess the impact of the change on key performance indicators, such as productivity, efficiency, and quality, to determine the overall success of the change initiative.
By monitoring these metrics, change management professionals can gauge the success of the change initiative and identify opportunities for further improvement. To read more about change adoption metrics check out The Comprehensive Guide to Change Management Metrics for Adoption.
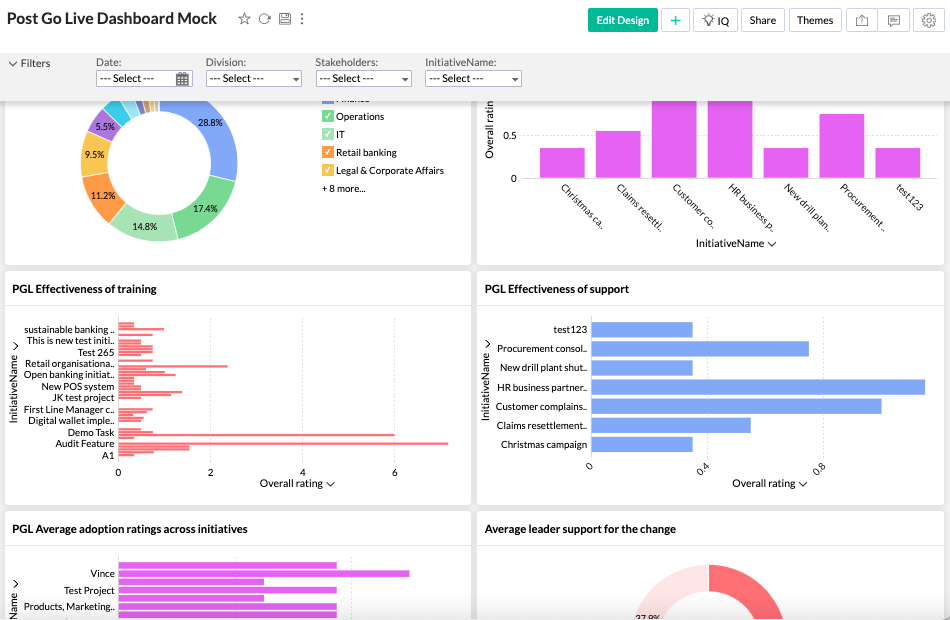
Change Impact and Capacity Metrics
Understanding the impact of change and the organization’s capacity to manage it is crucial for successful change management. Change impact metrics assess the effects of the change on the organization, while capacity metrics evaluate the organization’s ability to manage and sustain the change.
Change Impact Metrics
- Aggregate impacts: Aggregate impacts across initiatives to form a view of how various teams and roles are impacted by various changes.
- Risk Assessments: Identify potential risks associated with the change and evaluate their impact, ensuring that mitigation strategies are in place. A particular focus should be placed on business performance during change, across initiatives.
Capacity Metrics
- Resource Capacity: Assess the availability of resources, such as personnel, budget, and tools, to support the change initiative.
- Change Fatigue: Measure the risk for potential fatigue within the organization and its impact on stakeholders, ensuring that change initiatives are paced and driven appropriately.
- Support Structures: Evaluate the effectiveness of support structures, such as training programs, information hubs, and help desks, in facilitating the change. Support structures may also include change champion networks.
By assessing change impact and capacity, change management practitioners can ensure that the organization is well-equipped to manage and sustain the change initiative.
Change Maturity Assessment
Change maturity assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of the organization’s capability to manage change effectively. These assessments help identify strengths and weaknesses in the organization’s change management practices and provide a roadmap for improvement.
The Change Management Institute (CMI) Change Maturity Model is a comprehensive framework that takes a holistic approach to enhancing an organization’s change management maturity. It’s divided into three core functional domains, each playing a vital role in the overall journey toward maturity:
- Project Change Management
- Business Change Readiness
- Strategic Change Leadership.
These domains serve as the foundation for achieving higher levels of maturity within the organization.
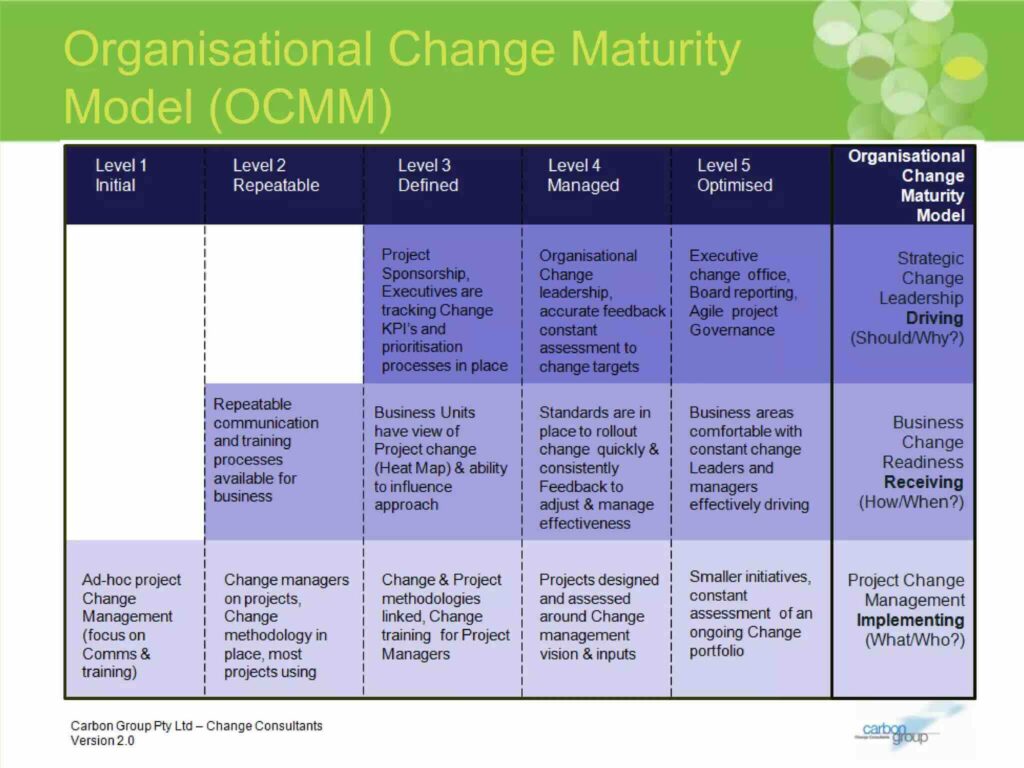
Within each of these domains, the CMI model outlines a structured path, consisting of five distinct maturity levels. These levels represent a continuum, starting at Level 1, which serves as the foundational stage, and progressing all the way to Level 5, the zenith of maturity and effectiveness. This multi-tiered approach offers organizations a clear roadmap for growth and development, ensuring that they have the tools and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of change management.
By conducting regular change maturity assessments, change management professionals can identify areas for improvement and develop targeted strategies to enhance the organization’s change management capability.
To read more about building Change Management Maturity check out this article.
The “Measure and Grow” principle is a powerful tool for improving change outcomes in a Scaled Agile environment. By leveraging data and fact-based decision-making, change management professionals can ensure that change initiatives are effective, aligned with strategic objectives, and continuously improving. Establishing robust metrics and assessment frameworks, such as KPIs, OKRs, change readiness and stakeholder engagement metrics, stakeholder competency assessments, change adoption metrics, change impact and capacity metrics, and change maturity assessments, is essential to applying the “Measure and Grow” principle effectively.
Incorporating these metrics and assessments into change management practices enables organizations to identify areas for improvement, make informed decisions, and drive continuous improvement. By doing so, change management professionals can enhance the effectiveness of change initiatives, ensure successful adoption, and ultimately achieve better business outcomes.