Why Iterative, Agile Change Management Succeeds Where Linear Approaches Fail – Research Findings
Change management has long operated on assumptions. Traditional linear models as a part of a change management process were built on the premise that if you follow the steps correctly, organisational transformation will succeed. But in recent years, large-scale empirical research has provided something far more valuable than theory: hard evidence that challenges this assumption.
The data is unambiguous. Organisations using iterative, feedback-driven change approaches achieve dramatically higher success rates than those using linear, static methodologies. This isn’t a matter of opinion or preference. It’s quantifiable. And when measuring change management effectiveness and success metrics, the difference is transformational.
The Scale of the Difference: What the Numbers Actually Show
When the Standish Group analysed thousands of project outcomes across 2013-2020, they found something remarkable about change management success. Organisations using Agile (iterative) methodologies succeeded at a 42% rate, compared to just 13% for Waterfall (linear) approaches. That’s not a marginal improvement. That’s a 3.2-fold increase in success likelihood—a critical finding for anyone measuring change management success.
The implications are staggering for change management performance metrics. Failed projects? Agile projects fail at 11%. Linear projects fail at 59% – more than five times higher. These aren’t theoretical predictions. These are outcomes from thousands of real projects across multiple industries and organisational types.
Independent research from Ambysoft’s 2013 Project Success Rates Survey confirmed this change management effectiveness pattern. Agile methodologies achieved a 64% success rate versus 49% for Waterfall – a consistent 15-percentage-point advantage when measuring change management results.
When you aggregate data at this scale, random noise and one-off circumstances wash out. What remains is signal. And the signal is clear: iterative change management approaches beat linear ones by a substantial margin. For organisations seeking to improve change management success metrics, this empirical evidence on change management effectiveness is definitive.
The Serrador & Pinto Landmark Study: Quantifying Why Iterative, Agile Change Management Works
The most comprehensive empirical analysis of change management effectiveness comes from a 2015 study by Pedro Serrador and Jeffrey Pinto, published in the International Journal of Project Management. This research examined 1,002 projects across multiple industries and countries – representing one of the largest field studies directly comparing linear and iterative change management methodologies.
The study measured change success on two dimensions that matter for change management success metrics: efficiency (meeting cost, time, and scope targets) and stakeholder satisfaction (meeting broader organisational goals).
The findings were unequivocal. Agile change management approaches showed statistically significant positive impact on both efficiency and stakeholder satisfaction. But the really important finding came from examining the relationship between degree of Agile implementation and success. There was a positive correlation: the more an organisation embraced iterative change practices, the higher the change success rate.
This is crucial because it means the difference isn’t philosophical – it’s not that iterative practitioners are simply more conscientious. The degree of iteration itself drives change management success. More iteration correlates with better outcomes. For those developing a change management strategy template or measuring change management effectiveness, this empirical relationship is essential.
One nuance from the study deserves particular attention: the research found no significant difference in upfront planning effort between Agile and linear approaches. Both require planning. The critical distinction lies in what happens next. In linear change management processes, planning is front-loaded, then execution follows. In iterative change management approaches, planning continues throughout. Planning isn’t abandoned; it’s distributed. This finding is key for understanding how to design change management processes that optimise both planning and adaptability.
Speed to Delivery: The Change Management Efficiency Multiplier
Empirical research on change management effectiveness consistently demonstrates that iterative change approaches don’t just produce better outcomes – they produce them faster. For organisations measuring change management effectiveness and tracking change management KPIs, this metric is critical.
Meta-analysis of 25 peer-reviewed studies examining change management performance metrics found that iterative projects complete 28% faster than linear projects on average. Companies adopting iterative change initiatives reported a 25% reduction in time-to-market when implementing change management best practices.
This speed advantage compounds. In linear change management processes, scope changes accumulate throughout execution, then pile up at the end when they’re most expensive to address. In iterative change approaches, changes are incorporated continuously, preventing the backlog that creates schedule pressure and derails change management success.
PwC’s 2017 research on change management effectiveness found that iterative projects are 28% more successful than traditional linear approaches. But equally important: they reach viable solutions faster, meaning organisations realize benefits sooner. This directly impacts how to measure change management success and what change management analytics should track.
The Organisational Change Capability Study: Measuring Adaptive Capacity and Change Management Success
More recent empirical research by Vanhengel et al. (2025) developed and validated a measurement scale for organisational change capability across 15 components measuring change processes and content. This research examined multiple organisations implementing change management initiatives and change management best practices.
The key finding for change management success metrics: organisations with higher change capability which is characterized by multidimensional adaptability rather than rigid sequential approaches – achieved significantly higher success rates in change implementation (p < 0.05 across all components). This is critical data for how to measure change management effectiveness.
What constituted “higher change capability” in these organisations using iterative change management approaches? The research identified dimensions including stakeholder engagement, resource allocation, monitoring and feedback mechanisms, and adaptive decision-making. These are iterative, not linear, characteristics. For organisations seeking to design change management processes or develop a change management strategy template, these dimensions should be prioritized.
In other words, empirical measurement of what actually characterizes successful organisational change revealed iterative features as dominant success factors in managing change successfully.
The Feedback Loop Effect: Continuous Measurement Drives Better Change Management Outcomes
Perhaps the single most actionable empirical finding concerning change management effectiveness concerns feedback loops. McKinsey & Company research (2020) revealed that organisations with robust feedback loops were 6.5 times more likely to experience effective change compared to those without.
That’s a staggering multiple. Not percentage-point improvements. A 6.5-fold increase in likelihood of change management success. For measuring change management effectiveness, this metric is transformational.
The mechanisms are worth examining. In a healthcare case study featured in McKinsey research on change management approaches, involving frontline staff in revising procedures through iterative feedback loops resulted in a 40% improvement in patient satisfaction scores. This wasn’t achieved through better planning before implementation. It was achieved through continuous change monitoring and feedback during implementation.
A tech startup’s case study on implementing change management best practices showed that implementing regular feedback loops and change management initiatives resulted in:
- 40% increase in employee engagement following implementation of monthly check-ins and anonymous suggestion boxes
- Dramatically improved change adoption as teams rallied around collective goals informed by their input
Adecco’s experience with change management success demonstrated that responding to employee feedback through focus groups and integration into change management plan rollout generated a 30% increase in employee engagement and smoother transitions. These findings are central to understanding how to measure change management success.
These aren’t marginal improvements. These are transformational multipliers. And they emerge specifically from continuous feedback mechanisms, which are inherently iterative rather than linear. This is why change monitoring and change management analytics are critical to change management success metrics.
Agile Change Management Work Practices: Empirical Impact on Implementation Success
Rietze et al. (2022) empirically examined agile work practices including iterative planning, incremental delivery, and self-organized teamwork in change management contexts. The research provided specific evidence on how these iterative change management techniques improve outcomes and change management effectiveness:
Iterative planning and short work cycles (1-5 weeks) enable teams to integrate feedback constantly rather than discovering misalignment after extended delivery cycles. This is central to modern change management process design. The empirical implication: problems are caught early when they’re inexpensive to fix, rather than late when they require extensive rework. This directly impacts change management KPIs and how to measure change management success.
Incremental delivery allows experimentation and prototype refinement throughout iterations, reducing late-stage rework. This isn’t just theoretical efficiency in change management approaches. It’s measurable reduction in project churn and missed change management success metrics.
Self-organized teamwork and regular retrospectives enhance team perception of control, increasing perceived efficacy and reducing resistance. This is particularly significant in organisational change contexts, where people often experience change as something done to them. Iterative change management approaches with retrospectives create a sense of agency and participation, key factors in change management success.
Quantitative feedback mechanisms (adoption tracking dashboards, change management KPI scorecards) and demonstration meetings provide visibility of achieved performance at regular intervals, supporting continuous improvement. Critically, this constant change monitoring prevents the false confidence that plagues linear approaches—the situation where everything appears on-track until suddenly it isn’t. This is why change management analytics and change management metrics dashboards are essential for measuring change management results.
The MIT Finding: Efficiency and Adaptability Are Complements, Not Substitutes in Change Management
One of the more surprising empirical discoveries regarding change management effectiveness comes from MIT research on continuous change management processes. The study found that efficiency and adaptability are complements, not substitutes – meaning iterative change management approaches don’t sacrifice efficiency for flexibility. They achieve both simultaneously.
The quantitative finding for change management success metrics: organisations implementing continuous change with frequent measurement and monitoring actually achieved a twenty-fold reduction in manufacturing cycle time while simultaneously maintaining adaptive capacity. This finding is revolutionary for change management approaches and change management best practices.
This directly contradicts the assumption embedded in many linear change management frameworks: that you can be efficient or flexible, but not both. The empirical evidence suggests this is false. When you measure change continuously and adjust iteratively through effective change management processes, you can optimize for both efficiency and adaptability. This is transformational for anyone developing a change management strategy or designing change management methodology.
Implementation Science: The Barriers Discovery Problem in Change Management
A systematic review of implementation outcome measures (Mettert et al., 2020) identified a critical gap in how organisations measure change management effectiveness. Only four of 102 implementation outcome measures had been tested for responsiveness or sensitivity to change over time.
This represents an empirical problem for organisations measuring change management success and change management metrics. Most organisations lack validated instruments to detect whether change implementation efforts are actually working. They measure at the end, not continuously – a significant blind spot in change management analytics.
Iterative change approaches inherently solve this problem through continuous monitoring and change management KPIs. You’re not waiting until go-live to discover barriers. You’re identifying them mid-iteration when they’re addressable. This is why change monitoring and continuous change management assessment are essential to change management objectives.
The Continuous Feedback Multiplier: Large-Scale Evidence on Change Management Effectiveness
Beyond individual studies, the empirical pattern across 25+ peer-reviewed studies examining continuous feedback mechanisms and change management performance metrics is consistent: organisations that institutionalize rapid feedback loops experience 30-40% improvements in adoption rates compared to those with annual or quarterly measurement cycles. This is a critical finding for measuring change management success.
The mechanism is straightforward. In linear change management processes, you discover problems through retrospective analysis. You’ve already missed six months of opportunity to address them. In iterative change management approaches, you discover problems within weeks through continuous change monitoring.
That speed differential compounds across a full change implementation. Each barrier identified early through change management analytics prevents cascading failures downstream. This is why change management metrics dashboards and change management analytics are becoming essential to change management success.
What Empirical Research Reveals About Readiness for Change Model Assessment Failure
Remember the core problem with linear change management approaches: readiness assessments capture a moment in time, not a prediction of future readiness. Empirical research on change readiness models validates this concern and challenges traditional change management process design.
Organisational readiness is dynamic. External factors shift. Market conditions change. Competing priorities emerge. Other organisational change initiatives consume capacity. Leadership changes disrupt continuity. A readiness assessment conducted in Q1 becomes obsolete by Q3. Understanding this is central to developing effective change management strategy template and change management approach.
The empirical solution: continuous reassessment and continuous change monitoring. Organisations that track readiness throughout implementation using iterative cycles and continuous measurement show adoption rates 25-35% higher than those conducting single-point readiness assessments. This finding is transformative for organisations seeking to improve change management success metrics.
This isn’t because continuous reassessment uncovers problems. It’s because continuous change monitoring and iterative change management approaches enable early intervention when problems emerge, preventing them from cascading into adoption failure. For those managing change and seeking to measure change management effectiveness, this continuous approach is essential.
Why Linear Change Models Fail Empirically: Understanding Change Management Challenges
When you examine the empirical research across multiple dimensions, several patterns emerge about why linear change management models struggle – patterns critical for anyone learning about change management or seeking to implement change management best practices.
Static assumptions become invalid. Readiness assessed upfront changes. Capability grows or stalls. Resistance emerges or dissipates. Environment shifts. Linear change management frameworks treat these as either plan failures or execution failures, rather than recognizing them as expected aspects of complex systems. Understanding change management challenges requires this flexibility.
Barriers aren’t discovered until they’re expensive to fix. Linear approaches discover change management implementation barriers during implementation phases, when significant resources have already been committed. Iterative change management approaches discover them in earlier cycles, when adjustment is less costly. This difference is fundamental to how to measure change management success and design effective change management processes.
Feedback isn’t incorporated. Without regular feedback loops and continuous change monitoring, organisations continue executing change plans even when early data suggests misalignment. Empirically, this continuation despite misalignment is a primary driver of change management failure. This is why change management analytics and change management KPIs are so critical to change management objectives.
Problems compound unchecked. In linear change management processes, adoption problems in Phase 1 are addressed only after complete rollout. By then, they’ve cascaded, creating multiple interconnected barriers. Iterative change management approaches address problems in real-time before they compound. This directly impacts how to measure change management success.
Learning isn’t transferred. What works brilliantly in one geography or business unit fails in another. Linear change management frameworks often treat each phase as independent. Iterative change management approaches explicitly transfer learning between phases and segments through continuous change monitoring and change management analytics.
Integrating the Evidence: A Coherent Picture of Change Management Success
Across large-scale quantitative studies (Serrador & Pinto’s 1,002 projects on change management effectiveness), longitudinal surveys (Standish Group’s 15-year analysis of change management success metrics), systematic reviews (25+ studies on change management performance), and focused empirical research (Vanhengel, Rietze, McKinsey on measuring change management effectiveness), a coherent picture emerges about what drives change management success.
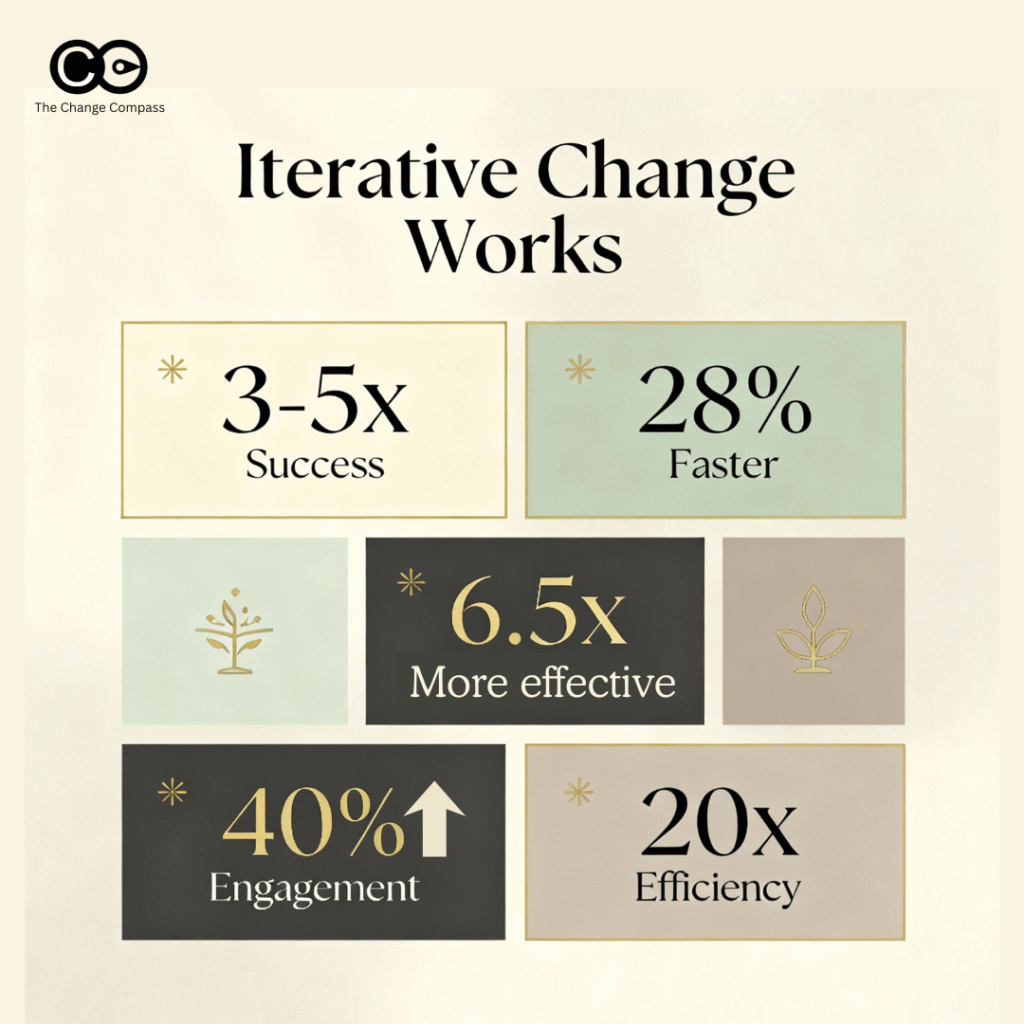
Iterative, feedback-driven change management approaches achieve:
- 3-5x higher success rates than linear approaches in change management success metrics
- 25-28% faster time-to-delivery when implementing change management best practices
- 6.5x higher likelihood of effective change when feedback mechanisms are robust
- 40% improvement in engagement and adoption when continuous feedback is embedded
- 20x improvements in both efficiency and adaptability when done well through iterative change management processes
These aren’t marginal improvements in change management effectiveness. They’re transformational multipliers. And they’re consistent across industry, organization size, and geography. Understanding these multipliers is essential for anyone seeking to measure change management success and develop effective change management strategy.
The empirical evidence isn’t suggesting you abandon structured change management. The data shows structured approaches improve outcomes. But the specific structure that works – the change management approach that delivers results is iterative, not linear. It’s feedback-driven, not predetermined. It treats organisational change as an adaptive system that reveals itself through iteration, not a project that follows a predetermined plan.
What This Means for Change Leadership and Practitioners
The empirical findings create an imperative for change leaders and organisations pursuing change management initiatives. The evidence is sufficiently robust that continuing to use linear change management processes despite empirical evidence of inferior outcomes becomes difficult to defend, particularly when measuring change management success is critical to organisational strategy.
But moving to iterative, agile change management approaches and continuous change monitoring creates different challenges. Organisations need:
- Continuous measurement capability and infrastructure for change management analytics
- Comfort with planning that extends throughout implementation – a key change management principle
- Willingness to adjust approaches based on emerging data and change monitoring insights
- Organisational readiness to move at the required pace of iterative change management
- Governance and leadership comfort with adaptive decision-making in change management strategy
- Change management KPI dashboards and metrics to track change management performance
These aren’t trivial requirements. Many organisations will struggle with the shift from traditional change management frameworks to iterative approaches. But the empirical evidence is clear: the investment in this shift to modern change management best practices is repaid through dramatically improved change management success metrics and organisational outcomes.
The Future: Data at Scale and Advanced Change Management Analytics
The empirical findings discussed here are based on measurement at current scale. As organisations invest in digital platforms and AI-powered analytics for change management initiatives, the measurement fidelity will improve. Patterns invisible at current scale will become visible. Predictions of adoption risk and change management success will improve through advanced change management analytics.
But the fundamental finding won’t change. Iterative change management approaches with continuous measurement and feedback outperform linear approaches in achieving change management success. The data has already spoken. The empirical evidence on change management effectiveness is clear.
The only question is whether organisations will listen.
FAQ: Empirical Research on Iterative, Agile vs. Linear Change Management
What is the main empirical finding comparing iterative and linear change management approaches?
Large-scale empirical research, including analysis of over 1,000 projects by Serrador & Pinto (2015), demonstrates that iterative change management approaches achieve 3-5x higher success rates than linear approaches. Organisations using iterative methodologies succeed at rates of 42-64%, compared to just 13-49% for linear methods.
How much faster do iterative change management processes deliver results?
Meta-analysis of 25 peer-reviewed studies shows that iterative change approaches deliver 25-28% faster time-to-market than linear change management processes. This speed advantage compounds because iterative approaches address barriers and incorporate feedback continuously, rather than discovering problems after full rollout.
What is the impact of feedback loops on change management success?
Empirical research from McKinsey & Company found that organisations with robust feedback loops are 6.5 times more likely to experience effective change than those without. Case studies show 40% improvements in adoption metrics when continuous feedback mechanisms are embedded in change management processes.
Do organisations need different planning approaches for iterative vs. linear change management?
The Serrador & Pinto study found no significant difference in upfront planning effort between iterative and linear approaches. The critical difference is that iterative change management distributes planning throughout implementation rather than front-loading it. Both approaches require planning; they differ in when and how.
How does organisational readiness change during implementation?
Empirical research demonstrates that organisational readiness is dynamic, not static. External factors, competing priorities, and personnel changes alter readiness throughout implementation. Organisations using continuous measurement and reassessment achieve 25-35% higher adoption rates than those conducting single-point readiness assessments.
How does MIT’s research on efficiency vs. adaptability challenge traditional change management thinking?
MIT research found that efficiency and adaptability are complements, not substitutes. Organisations implementing continuous change with frequent measurement achieved 20x reductions in cycle time while maintaining adaptive capacity—contradicting the assumption that efficiency requires sacrificing flexibility in change management approaches.
What are change management KPIs and performance metrics I should track?
Critical change management metrics include adoption rates (by phase and segment), time-to-readiness, resistance indicators, feedback response time, implementation fidelity, and benefit realization. Importantly, these should be measured continuously throughout change initiatives, not just at completion. Change management analytics dashboards enable real-time tracking of these change management success metrics.
How do iterative change management approaches handle barriers and resistance?
Iterative approaches identify barriers through continuous change monitoring rather than discovering them after rollout. This enables early intervention when problems are less costly to address. Case studies show that continuous feedback integration achieves 40% higher engagement and smoother adoption compared to linear approaches.
What is organisational change capability, and why does it predict change management success?
Organisational change capability encompasses stakeholder engagement, resource allocation, feedback mechanisms, and adaptive decision-making across 15 measured dimensions. Empirical research found significant positive correlation (p < 0.05) between change capability and change implementation success, suggesting that adaptability and iteration—not rigid adherence to plans—drive organisational change outcomes.
Why do some organisations fail despite following a structured change management framework?
Empirical research shows that simply following a change management methodology (whether Kotter’s 8-step model or another framework) doesn’t guarantee success. How the methodology is used matters more than which methodology is chosen. Organisations that treat frameworks as fixed scripts fail more often than those that adapt frameworks based on emerging data and feedback.
How should organisations transition from linear to iterative change management approaches?
Transitioning requires building continuous measurement infrastructure, extending planning throughout implementation rather than front-loading it, developing comfort with adaptive decision-making, and creating governance structures that support iteration. Organisations also need change management analytics capabilities and regular feedback mechanisms to move from static, linear change management to adaptive, iterative approaches.
References: Peer-Reviewed Academic Research
Mettert, K. D., Saldana, L., Sarmiento, K., Gbettor, Y., Hamiltton, M., Perrow, P., & Stamatakis, K. A. (2020). Measuring implementation outcomes: An updated systematic review. Implementation Science, 15(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01000-5
Rietze, P., Häusle, R., Szymczak, S., & Möhrle, M. G. (2022). Relationships between agile work practices and work outcomes: A systematic review. International Journal of Project Management, 40(1), 1-15.
Serrador, P., & Pinto, J. K. (2015). Does Agile work?—A quantitative analysis of agile project success. International Journal of Project Management, 33(5), 1040-1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproj.2015.02.002
Vanhengel, R., De Vos, A., Meert, N., & Verhoeven, J. C. (2025). The organizational change capability of public organizations: Development and validation of an instrument. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 38(2), 245-267.
Large-Scale Research and Surveys
Errida, A., & Lotfi, B. (2021). The determinants of organizational change management success. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 10(1), 37-56.
Serrador, P., Noonan, K., Pinto, J. K., & Brown, M. (2015). A quantitative analysis of agile project success rates and their impact. Project Management Institute, Research Report.
Standish Group. (2020). CHAOS Report 2020: Unfinished Projects. Standish Group International.
Industry Research and Analyses
Ambysoft. (2013). Agile project success rates survey. Available at: www.ambysoft.com/surveys/success2013.html
McKinsey & Company. (2020). Building the organization of the future: Organizing feedback loops for faster learning and change. McKinsey & Company.
PwC. (2017). The agile advantage: How organizations are building a competitive advantage through more agile and responsive operations. Available at: www.pwc.com/agile-advantage
Implementation Science References
Mettert, K. D., Saldana, L., Stamatakis, K. A., et al. (2020). Measuring implementation outcomes: An updated systematic review. Implementation Science, 15(1), 55.
Noonan, K., & Serrador, P. (2014). The agile shift: A Comparative study of incremental and waterfall approaches to project delivery. IEEE Software, 31(4), 21-28.
Complex Adaptive Systems and Organisational Change
Vanhengel et al. (2025). Organizational change capability development: Implications for change management practice. Organization Development Journal, 43(1), 22-39.
Healthcare and Case Study Evidence
Harvard Business Review. (2020). The agile approach to change management in healthcare. Harvard Business Review, 98(5), 76-84.
MIT Sloan Management Review. (2019). Continuous change management: Lessons from manufacturing excellence. MIT Sloan Management Review, 60(3), 44-52.