Change managers are not just facilitators of change transition; they are strategic partners who must understand and navigate complex organisational landscapes. One key skill that is often under-emphasised in this role is analytical capability. By adopting a strategic consultant’s mindset and employing robust analytical skills, change managers can significantly enhance their effectiveness throughout the project lifecycle. Let’s explore how change managers can leverage analytical skills at each phase of the project lifecycle, emphasising frameworks like MECE and TOSCA to drive successful change initiatives.
The Importance of an Analytical Lens
Change management involves facilitating transitions while ensuring that stakeholders are engaged and informed. However, to do this effectively, change managers must analyse complex data sets, identify patterns, and make informed decisions based on evidence. This analytical lens can be applied through every stage of the project lifecycle: commencement, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
Gone are the days when change practitioners are making recommendations ‘from experience’ or based on stakeholder input or feedback. For complex transformation, stakeholders now (especially senior stakeholders) demand a more rigorous, data-driven approach to drive toward solid change outcomes.
1. Project Commencement Phase
At the project commencement phase, the groundwork is laid for the entire change initiative. Change managers need to scan the organizational environment through the lens of impacted stakeholders, gathering relevant information and data.
Example: Consider a company planning to implement a new customer relationship management (CRM) system. The change manager should begin by analysing the existing state of customer interactions, assessing how the change will impact various departments such as sales, marketing, and customer service. This involves conducting stakeholder interviews, reviewing existing performance metrics, and gathering feedback from employees.
Using a MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) framework, the change manager can categorize stakeholder concerns into distinct groups—such as operational efficiency, user experience, and integration with existing systems—ensuring that all relevant factors are considered. By identifying these categories, the change manager can articulate a clear vision and define the desired end state that resonates with all stakeholders.
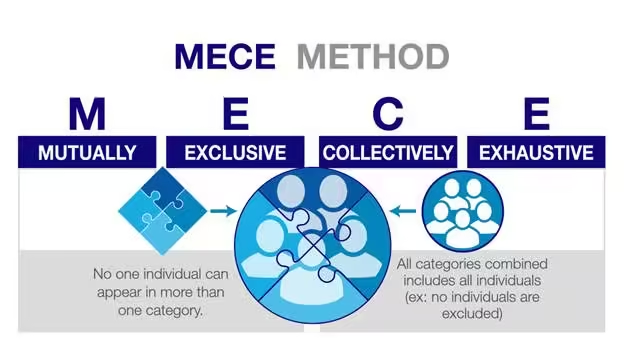
The above is from Caseinterview.com
Hypothesis: Sales Team Will Resist the New CRM System Due to Lack of Training and User-Friendliness
Step 1: Identify the Hypothesis
Hypothesis: The sales team will resist the new CRM system because they believe it is not user-friendly and they fear insufficient training.
Step 2: Break Down the Hypothesis into MECE Categories
To validate this hypothesis, we’ll break it down into specific categories that are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. We’ll analyse the reasons behind the resistance in detail.
Categories:
- User Experience Issues
- Complexity of the Interface
- Navigation Difficulties
- Feature Overload
- Training and Support Concerns
- Insufficient Training Programs
- Lack of Resources for Ongoing Support
- Variability in Learning Styles
- Change Management Resistance
- Fear of Change in Workflow
- Previous Negative Experiences with Technology
- Concerns About Impact on Performance Metrics
Step 3: Gather Data for Each Category
Next, we need to collect data for each category to understand the underlying reasons and validate or refute our hypothesis.
Category 1: User Experience Issues
- Data Collection:
- Conduct usability testing sessions with sales team members.
- Administer a survey focusing on user interface preferences and pain points.
- Expected Findings:
- High rates of confusion navigating the new interface.
- Feedback indicating that certain features are not intuitive.
Category 2: Training and Support Concerns
- Data Collection:
- Survey the sales team about their current training needs and preferences.
- Review existing training materials and resources provided.
- Expected Findings:
- Many team members express a need for more hands-on training sessions.
- A lack of available resources for ongoing support after the initial rollout.
Category 3: Change Management Resistance
- Data Collection:
- Conduct focus groups to discuss fears and concerns regarding the new system.
- Analyse historical data on previous technology implementations and employee feedback.
- Expected Findings:
- Employees voice concerns about how the CRM will change their current workflows.
- Negative sentiments stemming from past technology rollouts that were poorly managed.
Step 4: Analyse Data Within Each Category
Now that we have gathered the data, let’s analyse the findings within each MECE category.
Analysis of Findings:
User Experience Issues:
- Complexity of the Interface: Usability tests reveal that 70% of sales team members struggle to complete certain tasks in the CRM.
- Navigation Difficulties: Survey responses show that 80% find one step of the navigation counterintuitive, leading to frustration.
Training and Support Concerns:
- Insufficient Training Programs: Surveys indicate that only 40% of employees feel adequately trained to use this part of the new system.
- Lack of Resources for Ongoing Support: Focus groups reveal that team members are unsure where to seek help after the initial training.
Change Management Resistance:
- Fear of Change in Workflow: Focus group discussions highlight that 60% of participants fear their productivity will decrease with the new system, at least during the post Go Live period.
- Previous Negative Experiences: Historical data shows that past technology rollouts had mediocre adoption rates due to insufficient support, reinforcing current fears.
Step 5: Develop Actionable Recommendations
Based on the analysis of each category, we can create targeted recommendations to address the concerns raised.
Recommendations:
User Experience Issues:
- Conduct additional usability testing with iterative feedback loops to refine the CRM interface before full rollout.
- Simplify the navigation structure based on user feedback, focusing on the most frequently used features.
Training and Support Concerns:
- Develop a comprehensive training program that includes hands-on workshops, tutorials, and easy-to-access online resources.
- Establish a dedicated support team to provide ongoing assistance, ensuring team members know whom to contact with questions.
Change Management Resistance:
- Implement a change management strategy that includes regular communication about the benefits of the new system, addressing fears and expectations.
- Share success stories from pilot programs or early adopters to demonstrate positive outcomes from using the CRM.
By following this detailed step-by-step analysis using the MECE framework, the change manager can thoroughly investigate the hypothesis regarding the sales team’s resistance to the new CRM system. This structured approach ensures that all relevant factors are considered, enabling the development of targeted strategies that address the specific concerns of stakeholders. Ultimately, this increases the likelihood of successful change adoption and enhances overall organizational effectiveness.
Data-Driven Decision Making:
At this stage, change managers should work closely with the project sponsor and project manager to determine effective positioning. A data-driven approach allows the change manager to form a hypothesis about how the change will impact stakeholders. For instance, if data suggests that the sales team is particularly resistant to change, the manager might hypothesize that this resistance stems from a lack of understanding about how the new CRM will enhance their workflow.

2. Planning Phase
Once the project is initiated, the planning phase requires detailed strategy development. Here, analytical skills are essential for conducting stakeholder analysis and impact assessments.
Example: In our CRM implementation scenario, the change manager must analyse the data collected during the commencement phase to identify the specific impacts on different departments. This involves grouping and sorting the data to prioritize which departments require more extensive support during the transition.
Using the TOSCA (Target, Objectives, Strategy, Constraints, Actions) framework provides a structured approach to guide the change management process for the CRM implementation. This framework helps clarify the overall vision and specific steps needed to achieve successful adoption. Below is a detailed exploration of each component:
1. Target
Definition: The target is the overarching goal of the change initiative, articulating the desired end state that the organization aims to achieve.
Application in CRM Implementation:
- Target: Improve customer satisfaction and sales efficiency.
This target encapsulates the broader vision for the CRM system. By focusing on enhancing customer satisfaction, the organization aims to create better experiences for clients, which is crucial for retention and loyalty. Improving sales efficiency implies streamlining processes that enable sales teams to work more effectively, allowing them to close deals faster and serve customers better.
2. Objectives
Definition: Objectives are specific, measurable outcomes that the organization intends to achieve within a defined timeframe.
Application in CRM Implementation:
- Objectives: Increase customer retention by 20% within a year.
This objective provides a clear metric for success, enabling the organization to track progress over time. By setting a 20% increase in customer retention as a target, the change manager can align training, support, engagement and system adoption with this goal. This objective also allows for measurable evaluation of the CRM’s impact on customer relationships and retention efforts.
3. Strategy
Definition: The strategy outlines the high-level approach the organization will take to achieve the objectives. It serves as a roadmap for implementation.
Application in CRM Implementation:
- Strategy: Implement phased training sessions for each department, with tailored support based on the unique impacts identified.
This strategy emphasizes a thoughtful and structured approach to training, recognizing that different departments may face distinct challenges and needs when adapting to the new CRM. By rolling out training in phases, the organization can focus on one department at a time, ensuring that each team receives the specific support they require. Tailoring the training content based on the unique impacts identified earlier in the MECE analysis helps maximize engagement and effectiveness, addressing concerns about usability and fostering greater adoption of the CRM.
4. Constraints
Definition: Constraints are the limitations or challenges that may impact the successful implementation of the strategy. Recognizing these upfront allows for better planning and risk management.
Application in CRM Implementation:
- Constraints: Limited budget and time restrictions.
Acknowledging these constraints is critical for the change manager. A limited budget may affect the types of training resources that can be utilized, such as hiring external trainers or investing in advanced learning technologies. Time restrictions might necessitate a more rapid rollout of the CRM system, which could impact the depth of training provided. By recognizing these constraints, the change manager can plan more effectively and prioritize key areas that will deliver the most value within the available resources.
5. Actions
Definition: Actions are the specific steps that will be taken to implement the strategy and achieve the objectives.
Application in CRM Implementation:
- Actions: Develop a communication plan that includes regular updates and feedback mechanisms.
This action focuses on the importance of communication throughout the change process. A well-structured communication plan ensures that all stakeholders, particularly the sales team, are kept informed about the implementation timeline, training opportunities, and how their feedback will be incorporated into the process. Regular updates foster transparency and help build trust, while feedback mechanisms (such as surveys or suggestion boxes) allow team members to voice concerns and share their experiences. This two-way communication is essential for addressing issues promptly and reinforcing a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
By applying these frameworks, change managers can make informed recommendations that align with organizational objectives. This structured approach helps ensure that all relevant factors are accounted for and that stakeholders feel included in the planning process.
3. Execution Phase
As the project moves into the execution phase, the change manager must remain agile, continually collecting organizational data to confirm or reject the hypotheses formed during the planning stage.
Example: In an agile setting, where iterative processes are key, the change manager should implement mechanisms for ongoing feedback. For instance, after each sprint of CRM implementation, the manager can gather data from users to assess how well the system is being received. Surveys, usage analytics, and focus groups can provide rich insights into user experiences and pain points.
This ongoing data collection allows change managers to adjust their strategies in real-time. If feedback indicates that certain features of the CRM are causing confusion, the change manager can pivot to provide additional training or resources targeted specifically at those areas. This iterative feedback loop is akin to the work of strategic consultants, who continuously assess and refine their approaches based on empirical evidence.
Example in Practice: Imagine a situation where the sales team reports difficulties with the new CRM interface, leading to decreased productivity. The change manager can analyse usage data and user feedback to pinpoint specific issues. This data-driven insight can guide the development of targeted training sessions focusing on the problematic features, thus addressing concerns proactively and fostering user adoption.
4. Monitoring Phase
Monitoring the change initiative is crucial for ensuring long-term success. Change managers need to analyse performance metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation and its impact on the organization.
Example: For the CRM project, key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales conversion rates, customer satisfaction scores, and employee engagement levels should be monitored. By employing data visualization tools, change managers can easily communicate these metrics to stakeholders, making it clear how the change initiative is progressing.
A fact-based approach to analysing these metrics helps in making informed decisions about any necessary adjustments. If, for instance, customer satisfaction scores are declining despite an increase in sales, the change manager may need to investigate further. This might involve conducting interviews with customers or analysing customer feedback to identify specific areas for improvement.
Suppose the organization observes a drop in customer satisfaction scores following the CRM implementation. The change manager could work with other stakeholders to conduct a root cause analysis using customer feedback and service interaction data to identify patterns, such as longer response times or unresolved issues. By addressing these specific problems, the change manager can refine the CRM processes and enhance overall service quality.

5. Closure Phase
The closure phase involves reflecting on the outcomes of the change initiative and drawing lessons for future projects. This is where the analytical skills of change managers can shine in assessing the overall impact of the change.
Example: After the CRM system has been fully implemented, the change manager should conduct a comprehensive review of the project along with the project team (retro). This involves analysing both qualitative and quantitative data to evaluate whether the initial objectives were met. Surveys can be distributed to employees to gather feedback on their experiences, while sales data can be analysed to determine the financial impact of the new system.
Using frameworks like MECE can help in categorizing the lessons learned. For instance, feedback could be sorted into categories such as user experience, operational efficiency, and overall satisfaction, allowing the change manager to develop clear recommendations for future initiatives.
Lessons Learned: If the analysis shows that certain departments adapted more successfully than others, the change manager could investigate the factors contributing to this variance. For example, departments that received more personalized support and training may have demonstrated higher adoption rates. This insight can inform strategies for future change initiatives, emphasizing the importance of tailored support based on departmental needs.
Building Relationships with Senior Leaders
In addition to the technical aspects of change management, the ability to communicate effectively with senior leaders is crucial. Seasoned change managers must clearly understand organizational objectives and be able to articulate how the change initiative contributes to these goals.
Example: During discussions with senior leadership, a change manager along with the rest of the project team can present data showing how the CRM system has improved customer retention rates and increased sales. By positioning this information in an easily understandable and rigorous manner, the change manager demonstrates the value of the initiative and its alignment with broader organizational objectives.
Effective communication ensures that leaders remain engaged and supportive throughout the change process, increasing the likelihood of success. By continuously linking the change initiative to organizational goals, change managers can build trust and credibility with stakeholders at all levels.
Leveraging Analytical Frameworks
Throughout the project lifecycle, incorporating structured analytical frameworks can enhance the decision-making process. Here are two key frameworks that change managers can leverage:
MECE Framework
MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) helps in breaking down complex information into manageable parts without overlap. By ensuring that all categories are covered without redundancy, change managers can identify all relevant factors affecting the change initiative.
TOSCA Framework
TOSCA (Target, Objectives, Strategy, Constraints, Actions) provides a comprehensive roadmap for change initiatives. By clearly defining each component, change managers can develop coherent strategies that align with organizational goals. This framework not only clarifies the change strategy but also ensures that all team members understand their roles in achieving the objectives.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Change management is not a static process; it requires continuous learning and adaptation. As organizations evolve, change managers must stay attuned to emerging trends and best practices in the field. This involves seeking feedback, conducting post-project evaluations, and staying updated on analytical tools and methodologies.
Change managers can attend workshops, participate in industry conferences, and engage with professional networks to enhance their analytical skills and learn from peers. By sharing experiences and insights, change managers can refine their approaches and incorporate new strategies that drive successful change.
The Transformative Power of Analytical Skills
The role of a change manager is multifaceted and requires a broad range of skills. However, one skill that stands out as particularly critical is the ability to think analytically. By adopting a strategic consultant’s mindset and applying analytical skills at each phase of the project lifecycle, change managers can significantly enhance their effectiveness.
From project commencement to closure, employing frameworks like MECE and TOSCA allows change managers to approach challenges in a structured way, making informed decisions that drive successful change. Continuous data collection, stakeholder engagement, and effective communication with senior leaders are essential components of this analytical approach.
In an era where organizations must adapt quickly to change, the ability to analyse complex data sets and derive actionable insights will distinguish successful change managers from the rest. Emphasizing this critical skill not only positions change managers as strategic partners within their organizations but also ensures that change initiatives lead to lasting, positive transformations.
As change practitioners, let us elevate our analytical capabilities and drive impactful change with confidence and clarity. By embracing this essential skill, we can navigate the complexities of organizational change and lead our teams toward a successful future.






