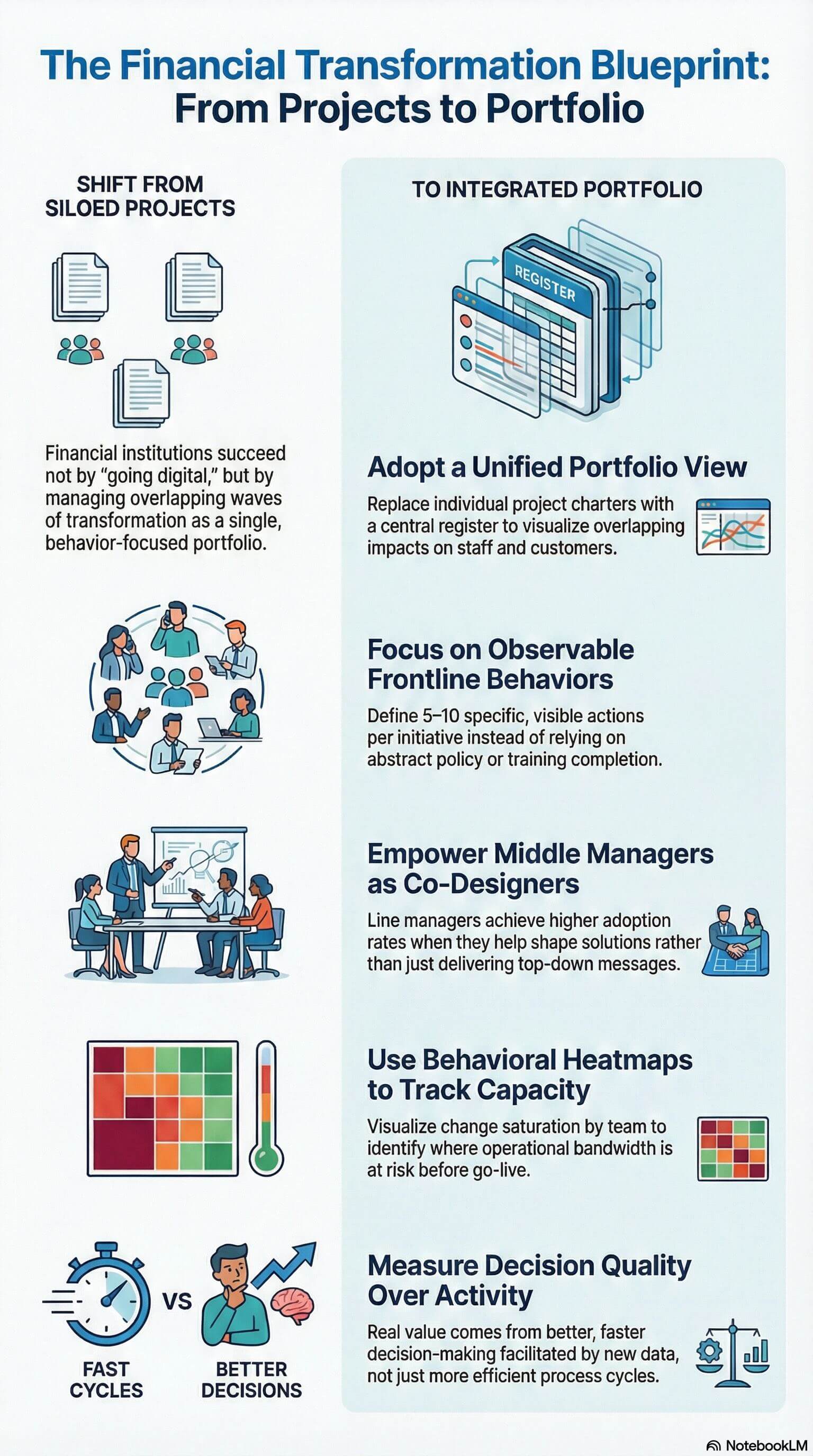
Do We Really Need a View of Changes Across the Organisation?
As the pace of change accelerates, senior leaders are increasingly asking for a comprehensive view of changes happening across the organisation. However, not everyone sees the need for this. Some change practitioners focus solely on project-level implementation, while others concentrate on developing change capability or leadership. So, is a broad organisational view of change necessary? The short answer is yes—and here’s why.
Why is a View of Changes Important?
1. Understanding Change is Key to Improving It
Managing change effectively requires a clear understanding of what is changing. Without visibility into the scope and nature of changes, how can we improve them? Imagine if Finance attempted to manage an organisation’s finances without access to financial data. The same principle applies to change management—without insights into ongoing changes, making informed improvements to how change is managed becomes impossible or at least ineffective.
A holistic view also helps identify patterns and systemic issues that may not be visible when looking at changes in isolation. For example, if multiple teams are experiencing resistance to similar types of change, it may indicate an underlying cultural or structural issue rather than a problem with individual initiatives.
2. Avoiding a Myopic View
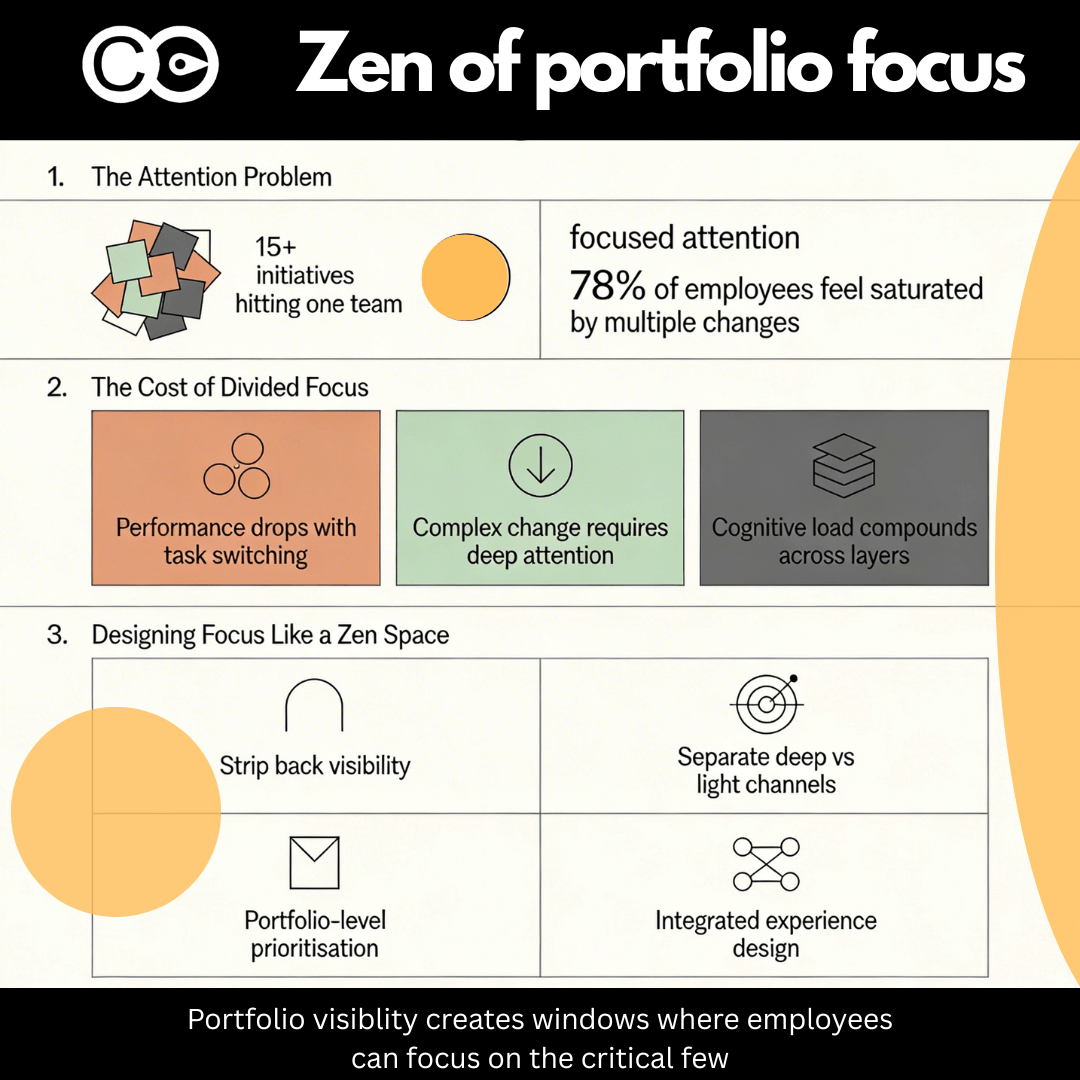
Many change practitioners operate at the project level, focusing on the change they are driving without visibility into other initiatives. This narrow focus can lead to conflicting priorities, resource constraints, and stakeholder fatigue. A fragmented approach often results in duplication of effort, where multiple teams work on similar initiatives without coordination, wasting time and resources.
A lack of visibility can also cause bottlenecks. For instance, two major transformation projects requiring input from the same group of employees may create undue pressure, leading to burnout and decreased productivity. With an organisational view, leaders can identify these risks in advance and implement measures to mitigate them, such as staggering implementation timelines or providing additional support.
3. Taking a Human-Centred Approach
A human-centred approach to change means viewing change from the perspective of impacted stakeholders rather than just from a project lens. Employees and customers experience multiple changes together, not in isolated silos. To design change experiences that work, we must understand the overall change landscape and how it affects people’s daily work and interactions.
Without a consolidated view, employees may feel overwhelmed by frequent, disconnected changes. This often leads to change fatigue, disengagement, and resistance. By considering how multiple changes intersect, organisations can design more coherent and supportive transition experiences for their people, improving adoption rates and overall satisfaction.
There are some who would rather not use the term ‘change fatigue’. Sure. Other labels may be used instead. However, not acknowledging its existence does not mean that it does not exists. We can choose to not label and not address the impacts of multiple changes. By doing this it will not magically go away. This is not going to help the business perform better and reach its targets.
4. Supporting Leadership in Managing Business Performance
Leaders are concerned about how changes impact business performance. Without a consolidated view of what is changing, how those changes interact, and their organisational impact, it is difficult to provide meaningful insights. A structured view of change enables leaders to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and optimise the overall change portfolio to support business objectives.
For example, if an organisation is rolling out a new customer relationship management (CRM) system while simultaneously restructuring its sales teams, leaders need to assess whether these initiatives will complement or hinder each other. Without this awareness, they may inadvertently introduce inefficiencies, such as duplicate training efforts or conflicting performance expectations.
5. Enhancing Organisational Readiness for Change
A key benefit of having a comprehensive view of change is improving organisational readiness. Readiness is not just about preparing individuals for a specific change but ensuring the organisation as a whole is capable of absorbing and adapting to continuous transformation.
An organisation that understands its change landscape can proactively assess its capacity for change at any given time. If several major initiatives are running concurrently, leaders can evaluate whether the organisation has the resources, cultural maturity, and leadership alignment to support them. Without this visibility, companies risk overloading employees and creating resistance due to excessive, poorly timed changes.
Furthermore, readiness assessments can identify gaps in capability, such as the need for additional training, clearer communication, or adjustments in leadership support. When organisations have a clear view of upcoming changes, they can put proactive measures in place, such as phased rollouts, targeted engagement efforts, or reinforcement mechanisms, to ensure smoother transitions and greater adoption success.
6. How an Integrated View of Change Supports Business Readiness
An integrated view of change enables organisations to move beyond reactive change management and embrace proactive change readiness. By mapping all significant transformations across the business, leaders can anticipate challenges, synchronise efforts, and prepare employees more effectively.
For example, if a company is implementing a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system while also shifting to a hybrid work model, an integrated change view allows decision-makers to assess whether these changes will create conflicting demands on employees. Instead of overwhelming teams with simultaneous process and technology shifts, adjustments can be made to stagger rollouts, align training programs, and provide tailored support.
Additionally, when businesses have a comprehensive perspective on change, they can implement readiness initiatives such as leadership coaching, employee engagement strategies, and resilience-building programs well in advance. This ensures that by the time changes take effect, the organisation is not just aware of them but fully prepared to embrace and sustain them. An integrated approach fosters a culture of adaptability, making the business more resilient in the face of continuous transformation.
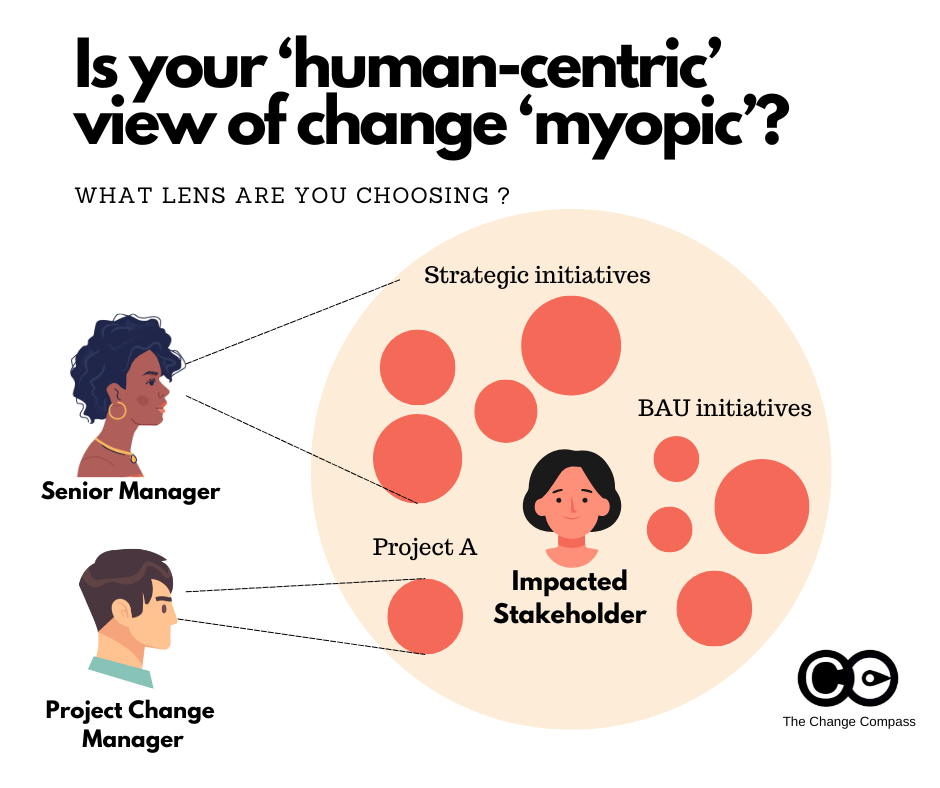
Addressing Common Concerns: “It’s Too Complicated”
A frequent argument against establishing an organisation-wide change view is that it is too complex and resource-intensive. However, this does not need to be the case.
1. Start Small and Scale Gradually
Instead of attempting a whole-organisation approach from the outset, begin with a stakeholder lens. Understand how changes impact specific stakeholder groups, then expand to teams, departments, and eventually the entire organisation. This phased approach ensures manageable progress without overwhelming stakeholders.
One way to do this is by focusing on a single high-impact function, such as IT or HR, and mapping their change landscape before expanding outward. By demonstrating value in a contained environment, it becomes easier to gain buy-in for broader adoption.
2. Begin with Basic Data
There is no need to start with an elaborate data set. A simple list of initiatives is enough to begin forming a picture. Over time, additional data points—such as timelines, affected stakeholders, and interdependencies—can be added to enhance visibility and analysis.
Many organisations already have elements of this data scattered across different departments. Consolidating this information in a central repository can be a quick win that provides immediate value without requiring extensive new processes.
3. Take an Agile, Iterative Approach
Building a change view incrementally allows for continuous refinement and adaptation. By adopting an agile mindset, practitioners can deliver immediate value while progressively enhancing the data set. This approach ensures that the effort remains practical and sustainable while demonstrating benefits to stakeholders at each stage.
Using lightweight collaboration tools, such as shared spreadsheets or simple dashboard software, can help kickstart the process without significant investment in complex change management platforms.
Once you progress to a more sophisticated level where you need AI support and advanced dashboarding, check out Change Compass.
The Benefits of an Organisational View of Change
1. Improved Stakeholder Experience
By understanding the cumulative impact of multiple changes, organisations can better manage stakeholder experiences. Employees are often subject to change saturation when faced with numerous uncoordinated initiatives. A holistic view enables better sequencing and pacing of change to ensure smoother transitions.
2. Enhanced Risk Management
Without an overarching view, risks associated with overlapping initiatives may go unnoticed until issues arise. Identifying potential bottlenecks and conflicts early helps in designing mitigating strategies before problems escalate. Risks may include program delivery risk, operational risk, benefit realisation risk and various people risks.
3. Better Resource Allocation
Organisations often face resource constraints, whether in terms of budget, personnel, or time. A consolidated view helps leaders prioritise initiatives effectively, ensuring that resources are allocated to high-impact changes while minimising inefficiencies.
4. Strengthened Leadership Decision-Making
Leaders require data-driven insights to make informed strategic decisions. A comprehensive change landscape provides clarity on what is happening across the organisation, empowering leaders to align transformation efforts with business objectives.
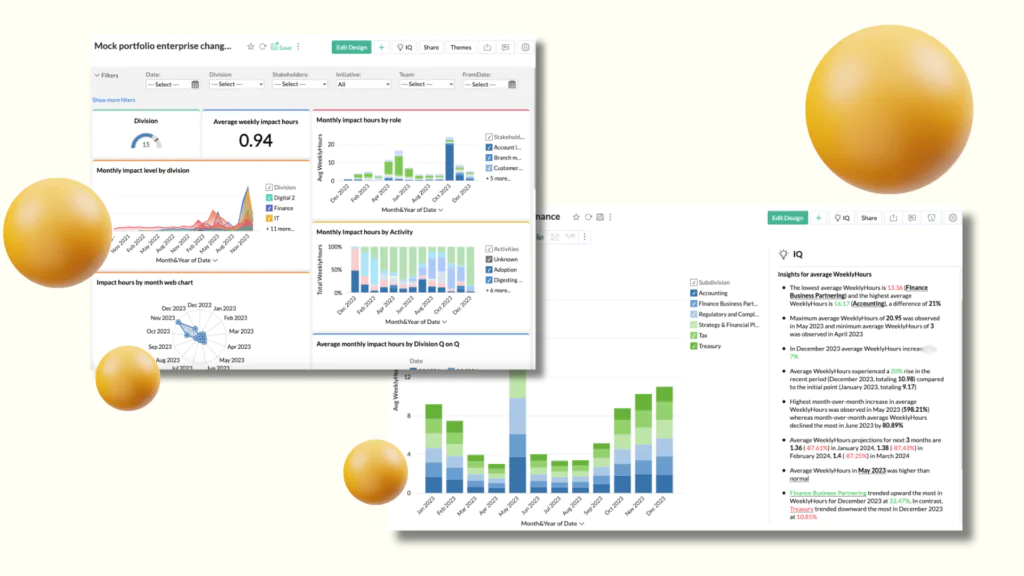
Practical Steps to Establish an Organisation-Wide Change View
Step 1: Identify Key Stakeholders
Begin by engaging stakeholders across the organisation to understand their concerns and expectations. These may include senior executives, department heads, project managers, and frontline employees.
Step 2: Map Current and Upcoming Changes
Compile a list of all ongoing and planned initiatives. Categorise them by business function, timeline, impacted teams, and strategic priority. This will create an initial snapshot of the change landscape.
Step 3: Identify Interdependencies
Assess how different initiatives interact with each other. Are there overlapping resource requirements? Do changes in one area impact another? Recognising these dependencies enables better coordination and minimises disruption.
Step 4: Develop a Change Portfolio View
Use visualisation tools to represent the collected data in a meaningful way. Heatmaps, Gantt charts, and stakeholder impact matrices can help illustrate the overall change picture.
Step 5: Implement Governance Structures
Establish governance mechanisms to continuously update and refine the change portfolio. This may involve periodic reviews, a centralised change coordination team, or designated change champions within each department.
Step 6: Communicate Insights Effectively
Share findings with stakeholders in a digestible format. Providing clarity on how changes align with organisational priorities fosters engagement and encourages proactive collaboration.
Future Trends in Organisational Change Visibility
1. Increased Use of Digital Tools
Advanced analytics, AI-driven insights, and dashboard visualisation tools are making it easier to track and analyse change across an organisation in real-time.
2. Integration with Business Strategy
Change management is increasingly being embedded within broader business strategy execution and performance metrics tracking, ensuring alignment with long-term goals.
3. Greater Focus on Employee Experience
Organisations are recognising the importance of measuring change from an employee perspective. This includes sentiment analysis, real-time feedback loops, and adaptive communication strategies.
A comprehensive view of change across an organisation is not just a ‘nice-to-have’—it is essential for effective change management. It enables better decision-making, reduces unintended consequences, and enhances the overall employee experience. While establishing such a view may seem complex, taking a pragmatic, step-by-step approach makes it achievable and valuable.
For experienced change and transformation professionals, this shift in perspective is not just about managing change—it’s about leading it effectively in an increasingly dynamic world.
To read more about creating your holistic view of change, check out Win over stakeholders with a single view of change in weeks and Approaches in deriving a single view of change