Air traffic control is one of the most sophisticated and high-stakes management systems in the world. Ensuring the safety of thousands of flights daily requires rigorous coordination, precise timing, and a structured yet adaptable approach. When failures occur, they often result in catastrophic consequences, as seen in the tragic January 2025 midair collision between an army helicopter and a passenger jet in Washington, D.C. airspace.
Think about the last time you took a flight. You probably didn’t worry about how the pilot knew where to go, how to land safely, or how to avoid other planes in the sky. That’s because air traffic control is a well-oiled machine, built on a foundation of real-time data, clear protocols, and experienced professionals making split-second decisions. Now, imagine if air traffic controllers had to work with outdated information, or if pilots had to rely on intuition rather than hard facts. Chaos, right?
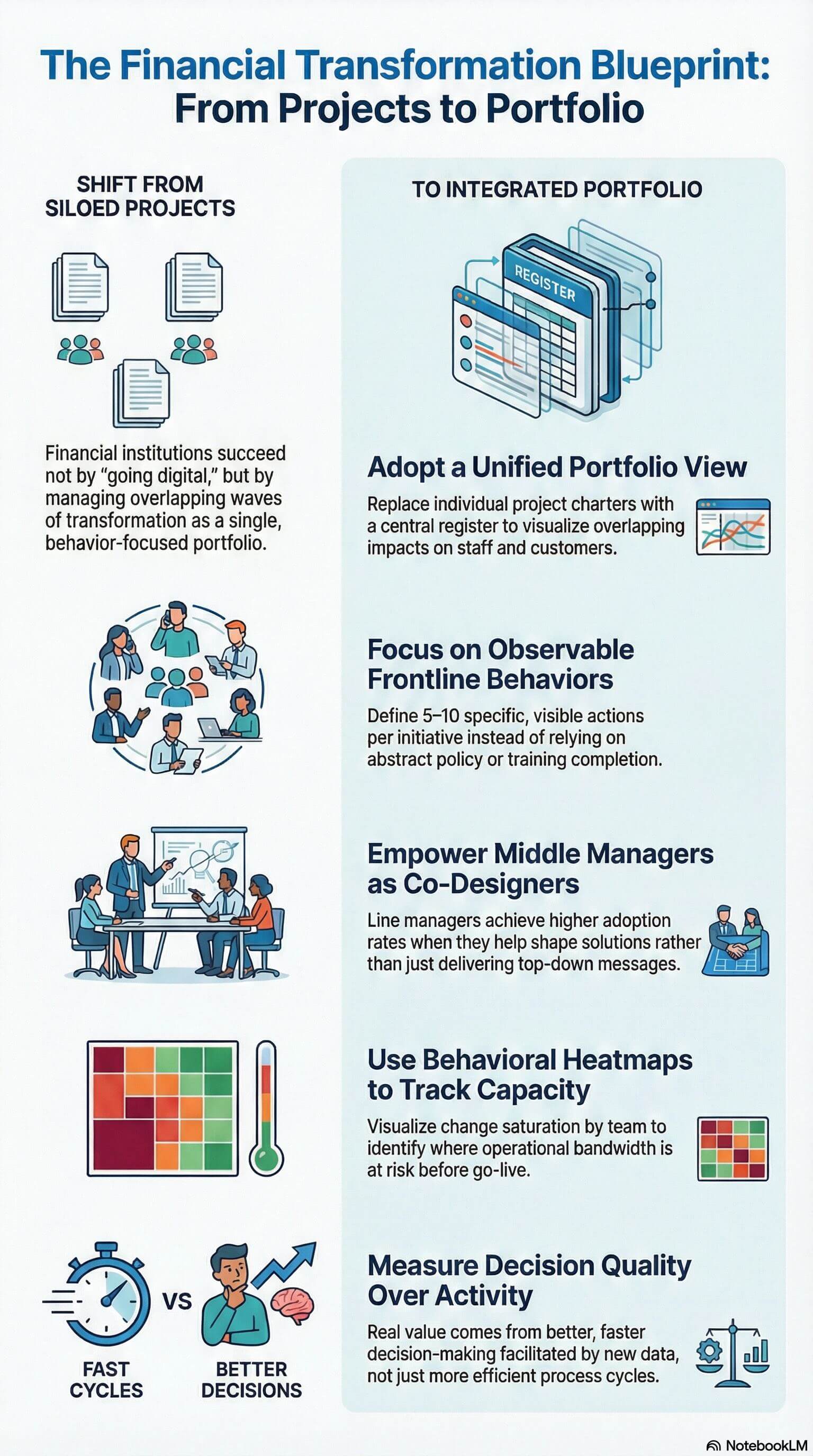
The same principles that apply to managing air traffic also hold valuable lessons for change and transformation management within organisations. Large-scale transformations involve multiple initiatives running in parallel, conflicting priorities, and significant risks. Without a structured, centralised approach, organisations risk failure, reduced value realisation, and employee fatigue.
The same logic applies to organisational change and transformation. Leaders are often trying to land multiple initiatives at once, each with its own trajectory, speed, and impact. Without real-time, accurate data, it’s all too easy for change initiatives to collide, stall, or overwhelm employees. Just as the aviation industry depends on continuous data updates to prevent disasters, businesses must embrace data-driven decision-making to ensure their transformation efforts succeed.
Here we’ll explore what air traffic control can teach us about using data effectively in change management. If you’ve ever felt like your organisation’s transformation efforts are flying blind, chaotic and uncoordinated, this one’s for you.
Lesson 1: The Danger of Overloading Critical Roles
The D.C. Midair Collision: A Case of Role Overload
In January 2025, a tragic midair collision occurred in Washington, D.C. airspace between an army helicopter and a passenger jet, claiming 67 lives. Investigations revealed multiple contributing factors, including inadequate pilot training, fatigue, insufficient maintenance, and ignored safety protocols. This incident underscored the dangers of overstretched resources, outdated processes, and poor data visibility—lessons that extend beyond aviation and into how organisations manage complex, high-stakes operations like change and transformation.
Additionally, the air traffic controller on duty was handling both helicopter and airplane traffic simultaneously, leading to a critical lapse in coordination. This split focus contributed to poor coordination and a lack of real-time situational awareness, ultimately leading to disaster. This is aligned with findings from various research that providing adequate resources is important in driving change and transformation.
Parallels in Change and Transformation Management
Organisations often suffer from similar overload issues when managing change. Many initiatives—ranging from business-as-usual (BAU) efforts to large-scale transformations—compete for attention, resources, and stakeholder engagement. Without a structured approach, teams end up working in silos, unaware of competing priorities or overlapping impacts.
There are some who argue that change is the new norm, so employees just need to get on the program and learn to adapt. It may be easy to say this, but successful organisations have learnt how to do this, versus ignoring the issue. After all, managing capacity and resources is a normal part of any effective operations management and strategy execution. Within a change context, the effects are just more pronounced given the timelines and the need to balance both business-as-usual and changes.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralised Oversight: Organisations need a structured governance model—whether through a Transformation Office, PMO, or Change Centre of Excellence—to track all initiatives and prevent “collisions.”
- Clear Role Definition: Initiative owners and sponsors should have a clear understanding of their responsibilities, engagement processes, and decision-making frameworks.
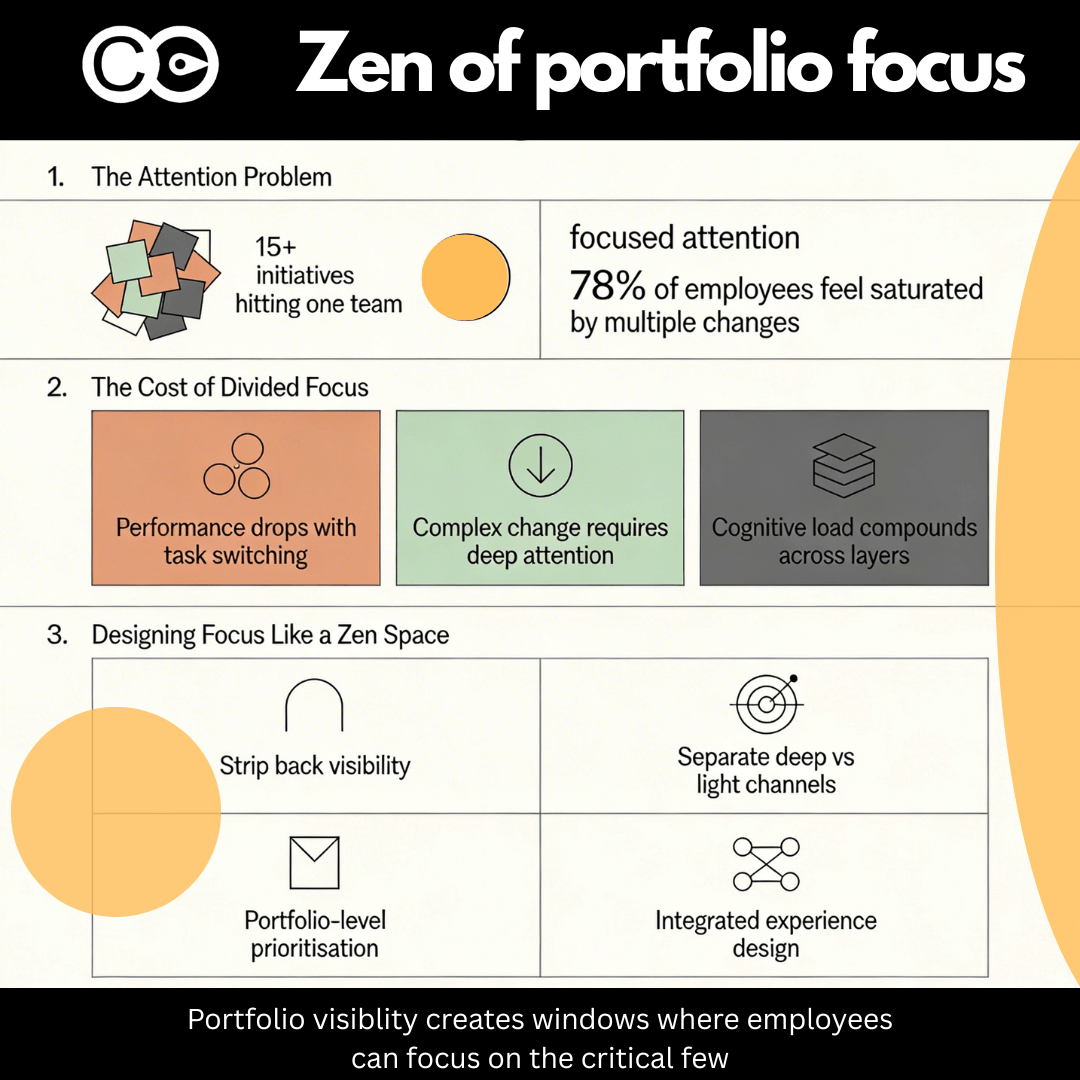
- Avoiding Initiative Overload: Employees experience “change fatigue” when multiple transformations run concurrently without proper coordination. Leaders must balance initiative rollout to ensure sustainable adoption.

Lesson 2: Providing Initiative Owners with Data-Driven Decision Autonomy
The UPS ‘Continuous Descent Arrivals’ System
UPS has been testing a data-driven approach to landings called ‘Continuous Descent Arrivals’ (source: Wall Street Journal article: Managing Air Traffic Control). Instead of relying solely on air traffic controllers to direct landing schedules, pilots have access to a full dashboard of real-time data, allowing them to determine their optimal landing times while still following a structured governance protocol. While CDA is effective during light traffic conditions, implementing it during heavy traffic poses technical challenges. Air traffic controllers must ensure safe separation between aircraft while optimising descent paths.
Applying This to Agile Change Management
In agile organisations, multiple initiatives are constantly iterating, requiring a balance between flexibility and coordination. Rather than centralised bottleneck approvals, initiative owners should be empowered to make informed, autonomous decisions—provided they follow structured governance (and when there is less risk of multiple releases and impacts on the business).
Key Takeaways:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Just as pilots rely on up-to-date flight data, organisations must have a transparent system where initiative owners can see enterprise-wide transformation impacts and adjust accordingly.
- Governance Without Bureaucracy: Pre-set governance protocols should allow for self-service decision-making without stifling agility.
- Last-Minute Adjustments with Predictability: Agile initiatives should have the flexibility to adjust their release schedules as long as they adhere to predefined impact management processes.
Lesson 3: Resourcing Air Traffic Control for Organisational Change
Lack of Air Traffic Controllers: A Root Cause of the D.C. Accident
The D.C. accident highlighted that understaffing was a critical factor. Insufficient air traffic controllers led to delayed decision-making and unsafe airspace conditions.
The Importance of Resource Allocation in Change and Transformation
Many organisations lack a dedicated team overseeing enterprise-wide change. Instead, initiatives operate independently, often leading to inefficiencies, redundancies, and conflicts. According to McKinsey, companies that effectively prioritise and allocate resources to transformation initiatives can generate 40% more value compared to their peers.
Key Takeaways:
- Dedicated Transformation Governance Teams: Whether in the form of a PMO, Transformation Office, or Change Centre of Excellence, a central function should be responsible for initiative alignment.
- Prioritisation Frameworks: Not all initiatives should receive equal attention. Organisations must establish structured prioritisation mechanisms based on value, risk, and strategic alignment.
- Investment in Change Capacity: Just as air traffic controllers are indispensable to aviation safety, organisations must invest in skilled change professionals to ensure seamless initiative execution.

Lesson 4: Proactive Risk Management to Prevent Initiative Collisions
The Risk of Unchecked Initiative Timelines
Just as midair collisions can occur due to inadequate tracking of aircraft positions, organisational change initiatives can “crash” when timelines and impacts are not actively managed. Without a real-time view of concurrent changes, organisations risk:
- Conflicting Business Priorities: Competing transformations may pull resources in different directions, leading to delays and reduced impact.
- Change Saturation: Employees struggle to absorb too many changes at once, leading to disengagement and lower adoption.
- Operational Disruptions: Poorly sequenced initiatives can create unintended consequences, disrupting critical business functions.
Establishing a Proactive “Air Traffic Control” for Change
- Enterprise Change Heatmaps: Organisations should maintain a real-time dashboard of ongoing and upcoming changes to anticipate and mitigate risks.
- Stakeholder Impact Assessments: Before launching initiatives, leaders must assess cumulative impacts on employees and customers.
- Strategic Sequencing: Similar to how air traffic controllers ensure safe landing schedules, organisations must deliberately pace their change initiatives.
The Role of Data in Change and Transformation: Lessons from Air Traffic Control
You Need a Single Source of Truth—No More Guesswork
Aviation Example: The Power of Integrated Data Systems
In aviation, pilots and controllers don’t work off scattered spreadsheets or conflicting reports. They use a unified system that integrates radar, satellite tracking, and aircraft GPS, providing a single, comprehensive view of air traffic. With this system, pilots and controllers can see exactly where each aircraft is and make informed decisions to keep everyone safe.
Application in Change Management: Why Fragmented Data is a Recipe for Disaster
Now, compare this to how many organisations manage change. Different business units track initiatives in separate spreadsheets, using inconsistent reporting standards. Transformation offices, HR, finance, and IT often operate in silos, each with their own version of the truth. When leaders don’t have a clear, real-time picture of what’s happening across the organisation, it’s like trying to land a plane in thick fog—without instruments.
Key Takeaways:
- Create a Centralised Change Management Platform: Just like air traffic control relies on a single system, organisations need a centralised platform where all change initiatives are tracked in real time.
- Standardise Data Collection and Reporting: Everyone involved in change initiatives should follow the same data standards to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Increase Visibility Across Business Units: Leaders need an enterprise-wide view of all change efforts to avoid conflicts and align priorities.

Real-Time Data Enables Agile, Confident Decision-Making
Aviation Example: UPS’s ‘Continuous Descent Arrivals’
UPS has a fascinating system for managing landings, known as ‘Continuous Descent Arrivals.’ Instead of waiting for air traffic controllers to dictate their landing time, pilots receive real-time data about their approach, runway conditions, and surrounding traffic. This allows them to determine the best landing time themselves—within a structured framework. The result? More efficient landings, less fuel waste, and greater overall safety.
Application in Change Management: The Danger of Outdated Reports
Too often, business leaders make transformation decisions based on data that’s weeks—or even months—old. By the time they realise a problem, the initiative has already veered off course. When leaders lack real-time data, they either act too late or overcorrect, causing further disruptions.
Key Takeaways:
- Use Live Dashboards for Initiative Management: Just as pilots rely on real-time flight data, change leaders should have constantly updated dashboards showing initiative progress, risks, and dependencies.
- Empower Initiative Owners with Data-Driven Autonomy: When given up-to-date information, initiative owners can make faster, smarter adjustments—without waiting for top-down approvals.
- Leverage Predictive Analytics to Anticipate Challenges: AI-driven insights can flag potential risks, such as change saturation or conflicting priorities, before they become full-blown issues.
Data-Driven Risk Mitigation—Preventing Initiative Collisions
Aviation Example: Collision Avoidance Systems
Modern aircraft are equipped with automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) systems, which allow them to communicate real-time flight data with each other. If two planes are on a collision course, these systems warn pilots, giving them time to adjust. It’s a proactive approach to risk management—problems are detected and resolved before they escalate.
Application in Change Management: Avoiding Crashes Between Initiatives
In organisations, multiple change initiatives often roll out simultaneously, each demanding employee attention, resources, and operational bandwidth. Without real-time risk monitoring, it’s easy to overwhelm employees or create operational bottlenecks. Many organisations don’t realise there’s an issue until productivity starts dropping or employees push back against the sheer volume of change.
Key Takeaways:
- Invest in Impact Assessment Tools: Before launching an initiative, leaders should evaluate its potential impact on employees and the business.
- Run Scenario Planning Exercises: Like pilots in flight simulators, organisations should model different change scenarios to prepare for potential challenges.
- Set Up Early Warning Systems: AI-driven analytics can detect overlapping initiatives, allowing leaders to intervene before issues arise.
The High Cost of Inaccurate or Delayed Data
Aviation Example: The D.C. Midair Collision
The tragic January 2025 midair collision in Washington, D.C. was, in part, the result of outdated and incomplete data. A single air traffic controller was responsible for both helicopter and airplane traffic, leading to a dangerous lapse in coordination. Miscommunication about airspace restrictions only made matters worse, resulting in an avoidable catastrophe.
Poor Data Leads to Costly Mistakes
The corporate equivalent of this is when transformation teams work with old or incomplete data. Decisions based on last quarter’s reports can lead to wasted resources, poorly sequenced initiatives, and employee burnout. The consequences might not be as immediately tragic as an aviation disaster, but the financial, momentum and cultural costs can be devastating.
Key Takeaways:
- Prioritise Frequent Data Updates: Change leaders must ensure initiative data is refreshed regularly to reflect real-time realities.
- Collaborate Across Functions to Maintain Accuracy: Transformation leaders, HR, finance, and IT should work together to ensure all change impact data is reliable.
- Automate Reporting Where Possible: AI and automation can reduce human error and provide real-time insights without manual effort.
Balancing Automation with Human Judgment
Aviation Example: Autopilot vs. Pilot Oversight
While modern planes rely heavily on autopilot, pilots are still in control. They use automation as a support system, but ultimately, human judgment is the final safeguard. It’s the perfect balance—automation enhances efficiency, while human oversight ensures safety.
Some leaders may find the process of collecting and analyzing data cumbersome, time-consuming, and even unnecessary—especially when they’re focused on quick execution. Gathering accurate, real-time data requires investment in tools, training, and disciplined processes, which can feel like an administrative burden rather than a value driver.
However, the benefits far outweigh the effort. A well-structured data system provides clarity on initiative progress, prevents conflicting priorities, enhances decision-making, and ensures resources are allocated effectively. Without it, organisations risk initiative overload, employee burnout, wasted budgets, and ultimately, failed transformations. Just like in aviation, where poor data can lead to fatal accidents, a lack of real-time insights in change management can result in costly missteps that derail business success.
Moreover, having an integrated process whereby data regularly feeds into decision making, as a normal business-as-usual process, builds the overall capability of the organisation to be a lot more agile and be able to change with confidence.
Navigating Change with Data-Driven Precision
Aviation has shown us what happens when decision-makers lack real-time, accurate data—mistakes happen, and consequences can be severe. In organisational change, the same principles apply. By embracing real-time data, predictive analytics, and structured governance, companies can navigate change more effectively, preventing initiative overload, reducing resistance, and maximising impact.
Ultimately, the goal is simple: Ensure your change initiatives don’t crash and burn. And just like in aviation, data is the key to a smooth landing.
To read more about managing change saturation check out How to Manage Change Saturation using this ancient discipline and How to measure change saturation
To read more about managing multiple changes or a change portfolio check out our various articles here.
If you would like to chat more about how to utilise a digital/AI solution that will equip you will insightful data to make critical business decisions in your air traffic control of your changes, reach out to us here.