Change management is an intricate dance between vision, strategy, execution, and perhaps most importantly, adoption. The ultimate goal of any change initiative is not merely to implement new systems, processes, or regulations but rather to embed these changes into the very fabric of the organization, ensuring widespread adoption and long-term sustainability.
Adoption metrics provide the critical tools organizations use to measure how well individuals embrace these changes, how behaviours evolve over time, and ultimately, how the change initiative impacts business outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, you will discover essential adoption metrics, principles of effective measurement, practical strategies for monitoring behaviours, and how to build dashboards that deliver actionable insights.
What Are Change Management Adoption Metrics?
Change management adoption metrics are quantifiable indicators that help organizations track the extent to which employees, teams, and other stakeholders successfully embrace and sustain changes introduced by transformation initiatives.
These metrics go beyond superficial indicators like training attendance or initial rollout success. Instead, they focus on meaningful outcomes that show real adoption, including:
- User engagement rates: How actively users interact with new systems or processes.
- Feature usage: Frequency and depth at which specific tools or functions are utilized.
- Retention rates: Sustained use over time, indicating lasting adoption.
- Behavioural compliance: Adherence to new workflows, policies, or regulatory behaviours.
- Customer feedback: External perceptions of service or product improvements due to change.
Tracking these metrics allows organizations to understand adoption success, spotlight issues early, and continuously refine change strategies to drive greater impact.
Fundamental Principles of Measuring Adoption
Context Matters
Every change initiative is unique. Different organizational cultures, leadership styles, industries, and change scopes mean no two adoption measurement approaches are identical. Tailoring metrics to align with your initiative’s objectives, stakeholder dynamics, and organizational readiness ensures relevance and maximizes insights.
Focus on Outcomes
Effective adoption metrics focus on measuring outcomes and impact rather than just tracking inputs or activities. For example, instead of simply counting training session attendance, measure whether the training led to proficiency improvements, behaviour changes, or feature activations.
Continuous Monitoring
Adoption isn’t a one-time milestone but an ongoing process. Continuously monitoring adoption metrics over the lifecycle of the change initiative helps detect drops or resistance early, allowing course corrections before issues become entrenched.
Use Multiple Data Sources
Triangulate data across system logs, surveys, interviews, observations, and feedback channels. Combining quantitative system metrics with qualitative insights from stakeholders gives a holistic view of adoption progress.
Measure at Multiple Levels
Track adoption metrics at individual, team, process, and organizational levels to understand how change permeates through various layers and identify bottlenecks or champions.
Key Adoption Metrics for System Implementations
System implementation projects, such as rolling out a new CRM, ERP, or productivity tool, often represent significant organizational investments. Measuring adoption effectively is vital to ensure these investments deliver value.
Below are the most impactful metrics to track:
System Feature Usage Frequency
This metric measures how often different features of the new system are used by employees. High usage of core functionalities indicates engagement and proficiency, while low usage signals training or usability gaps.
Example: Track daily active users (DAU) leveraging key features and compare to expected adoption benchmarks.
Process Efficiency Gains
Measure improvements in process cycle times, throughput rates, and resource utilization resulting from system adoption. Efficiency gains indicate that new workflows powered by the system are being embedded effectively.
Example: Average time to complete a sales order before and after system launch.
Customer Conversation Audit
For systems impacting customer interactions (e.g., customer service platforms), auditing conversations for quality and completeness helps track whether adoption translates to better client experiences.
Example: Percentage of calls with complete data logged, sentiment improvement metrics.
Sales Volume Changes
Tracking changes in sales or revenue post-implementation demonstrates the monetary impact of system adoption. Correlate with feature usage and process compliance data for deeper insights.
Example: Monthly sales growth percentage compared to prior periods.
Information Completeness
Quantify how well the system captures comprehensive and accurate data. High data quality supports better decisions and downstream workflows.
Example: Percent of customer records with complete contact and interaction histories.
Customer Satisfaction Scores
Survey customers on their experience after the system adoption to assess satisfaction gains linked to the change.
Example: Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer satisfaction index before and after rollout.
Pro Tips for System Implementation Metrics
Segment metrics by user roles and departments to identify adoption disparities.
Focus on the critical few features driving business outcomes rather than every system capability.
Use adoption trend charts over time rather than static snapshots for better story-telling with data.

Key Adoption Metrics for Compliance Initiatives
Compliance initiatives are critical for organizations to meet regulatory standards, industry certifications, or internal policies. Measuring adoption here ensures risks are minimized and consistent behaviours are embraced.
Process Compliance
This metric tracks adherence to defined regulatory processes and standards. High compliance levels reflect successful adoption of mandatory behaviours.
Example: Percent of audit checklist items fully completed within prescribed timelines.
Rated Compliance of Targeted Behaviours
Evaluate employee compliance with specific prescribed behaviours affected by regulatory changes. This can be measured through self-assessments, manager evaluations, or external audits.
Example: Percentage of staff consistently applying new data privacy protocols.
Frequency of Team Leader Coaching
Track how often supervisors provide coaching and reinforcement of compliance behaviours. Regular coaching boosts awareness and accountability.
Example: Number of coaching sessions conducted per month per team.
Customer Feedback on Compliance
Collect feedback from customers or clients regarding their experiences with the organization’s compliance posture post-change.
Example: Customer ratings on service adherence to privacy and security standards.
Number of Incidents
Monitoring incidents related to non-compliance serves as an early warning system to detect gaps before they escalate.
Example: Incident count reduction trend over quarters after policy rollout.
Key Adoption Metrics for Restructuring Initiatives
Restructuring initiatives, such as mergers, realignments, or downsizing, profoundly impact employee morale and organizational performance. Analytics here help assess adoption and foster alignment with new structures.
Employee Engagement and Morale
Measure changes in engagement and morale through surveys, interviews, and focus groups pre- and post-restructuring.
Example: Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) variations over the restructuring timeline.
Organizational Alignment
Evaluate how well the restructuring aligns with strategic objectives by tracking KPIs like revenue growth, market share, and customer satisfaction.
Example: Changes in strategic goal attainment percentages post-merger integration.
Communication Effectiveness
Assess clarity, frequency, and impact of communication during restructuring via employee feedback.
Example: Percent of employees rating communication as clear and timely.
Employee Productivity and Performance
Monitor turnover rates, absenteeism, and performance evaluations over time to understand restructuring impact on workforce productivity.
Example: Decrease in voluntary turnover six months post-restructuring.
Leadership Effectiveness
Gather employee ratings of leadership communication, decisiveness, and supportiveness during change.
Example: Improvement in leadership trust scores in post-restructuring surveys.
Team Dynamics and Collaboration
Evaluate collaboration metrics and cross-functional cooperation to identify strengths and weaknesses impacting adoption.
Example: Frequency of cross-team projects and collaboration tool usage statistics.
Implementing and Measuring Adoption Metrics
Successfully measuring adoption requires a disciplined approach:
-
Define Clear and Measurable Objectives: Identify behaviour changes and outcomes critical for the initiative’s success. Set quantifiable goals aligned with these objectives.
-
Select Relevant Metrics: Choose metrics that are actionable, observable, and tied directly to desired behaviours or outcomes.
-
Utilize Multiple Data Sources: Collect data from system logs, surveys, interviews, observations, and feedback to get a comprehensive picture.
-
Monitor Progress Continuously: Establish real-time dashboards or regular reporting cadences to track trends and detect issues.
-
Provide Timely Feedback and Support: Deliver actionable insights to managers and change agents to reinforce positive behaviours or address gaps.
-
Iterate and Adapt: Use ongoing insights to refine measurement approaches and adoption strategies dynamically.
Measuring Micro-Behaviours in System Implementations
Micro-behaviours are the small, observable actions employees take that directly influence successful adoption at the operational level. Measuring these gives deeper insight than high-level outcomes alone.
User Interface Navigation
Track how proficiently employees navigate new software, including time taken to complete tasks and error rates. Frequent help requests indicate areas of friction.
Example Metric: Average clicks to complete a key transaction; number of help desk tickets per task.
Data Entry Accuracy
Measure precision and completeness of data input, reflecting adherence to new standards and training effectiveness.
Example Metric: Percent of customer records flagged for errors or omissions.
Workflow Integration
Assess usage of new tools in daily work routines compared to legacy processes.
Example Metric: Ratio of transactions processed via new system vs. manual methods.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Monitor participation in collaborative platforms, document sharing, and informal knowledge networks.
Example Metric: Number of active contributors to shared knowledge bases.
Adoption of Best Practices
Track compliance with recommended workflows and procedures designed to optimize new systems.
Example Metric: Rate of adherence to standardized templates or checklists.
Change Agent Engagement
Measure the involvement of designated change champions in driving adoption through training, communications, and peer support.
Example Metric: Frequency of training sessions led; engagement survey ratings for champions’ effectiveness.
Pro Tips for Micro-Behaviour Metrics
-
Combine quantitative data with qualitative input (e.g., feedback from change champions) to contextualize numbers.
-
Use micro-behaviour metrics to diagnose root causes of adoption issues quickly.
-
Highlight micro-behaviours as actionable areas rather than abstract outcomes for clearer communication with teams.
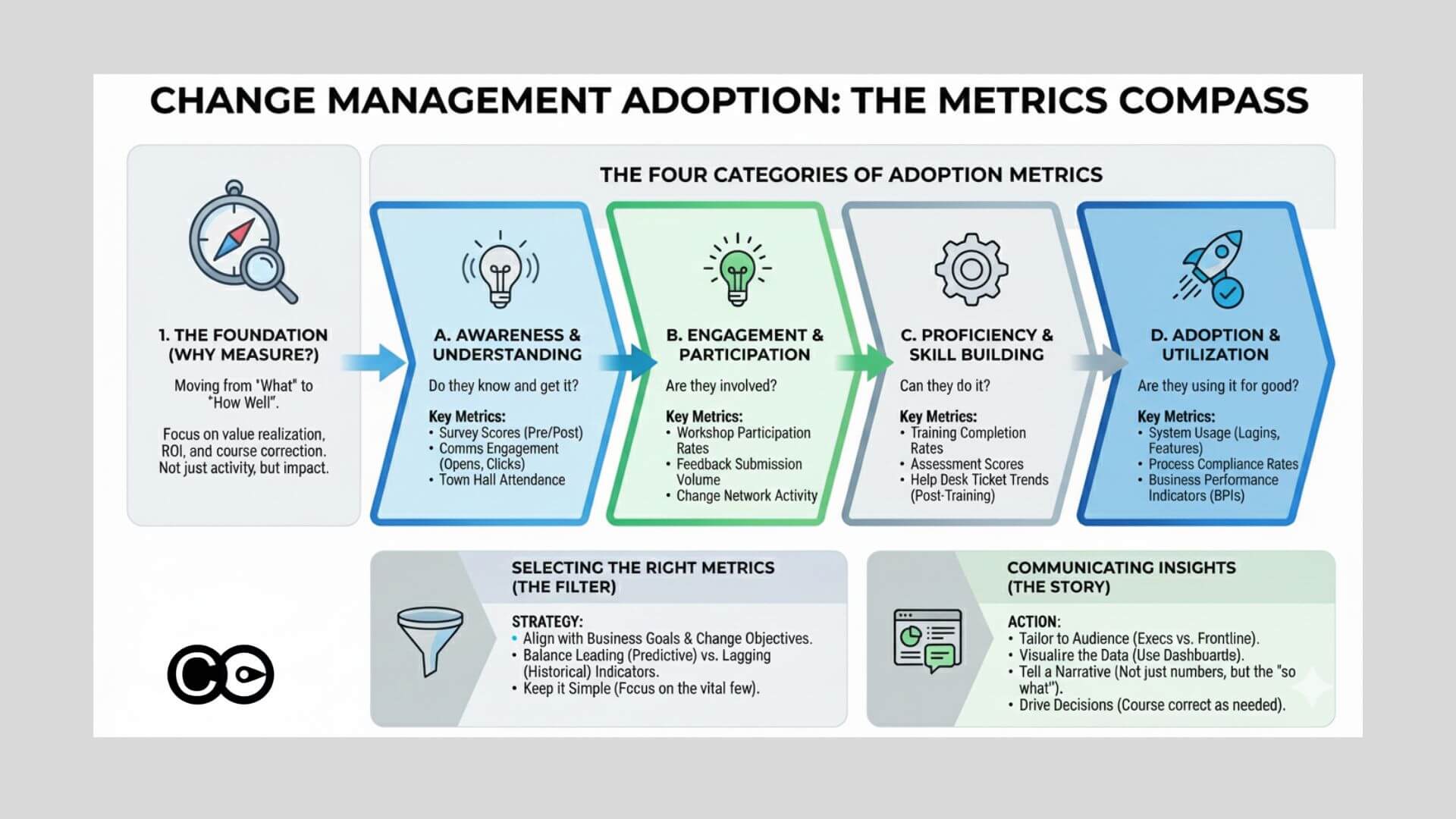
How Many Adoption Metrics Should You Track?
When it comes to measuring behaviour change in change initiatives, the old adage “less is more” is especially true. While it’s tempting to track a multitude of metrics to capture every nuance, focusing on the critical few behaviours that drive the greatest impact is essential for clarity and actionable insights.
Focus on Key Objectives
Start by identifying the core outcomes your change initiative aims to achieve — whether increased system usage, improved compliance, enhanced morale, or customer satisfaction. Align your metric selection tightly to these objectives.
Prioritize High-Impact Behaviours
Narrow down to a manageable set of metrics that capture the behaviours most likely to influence success. Typically, 8 to 15 core metrics, carefully grouped by outcome area, strike a good balance.
Consider Manageability and Data Availability
Avoid overwhelming your teams or diluting focus by tracking too many metrics. Ensure selected metrics are feasible to collect accurately and regularly.
Use Both Quantitative and Qualitative Metrics
Combine objective data (completion rates, error counts, usage stats) with qualitative insights (surveys, interviews) for a rich, holistic measurement approach.
Account for Interdependencies
Recognize that behaviours are interconnected; changes in one area may affect others. Select metrics that capture key interactions or cascading effects when possible.
Brand Alignment and Voice Recommendations
-
Maintain a clear, authoritative but approachable tone aimed at practitioners and organizational leaders.
-
Use customer-centric language that emphasizes measurable outcomes and business value.
-
Reference reputable frameworks and expert perspectives (such as Prosci) to build trust and credibility while showcasing your unique comprehensive metric approach.
-
Align terminology clearly across all change management topics to reinforce consistency.
-
Integrate and explicitly reference existing infographics or tables to maintain visual continuity and ease of understanding.
Infographic and Visual Asset Preservation
The article contains key infographics summarizing metrics across major initiative categories:
-
System Implementation Metrics
-
Compliance Metrics
-
Restructuring Metrics
-
Micro-behaviour Metrics
Ensure all metric names and groupings in the text match these visuals perfectly to allow reuse without redesign. Link explicitly to these assets when discussing metric groups to reinforce learning and support presentations.
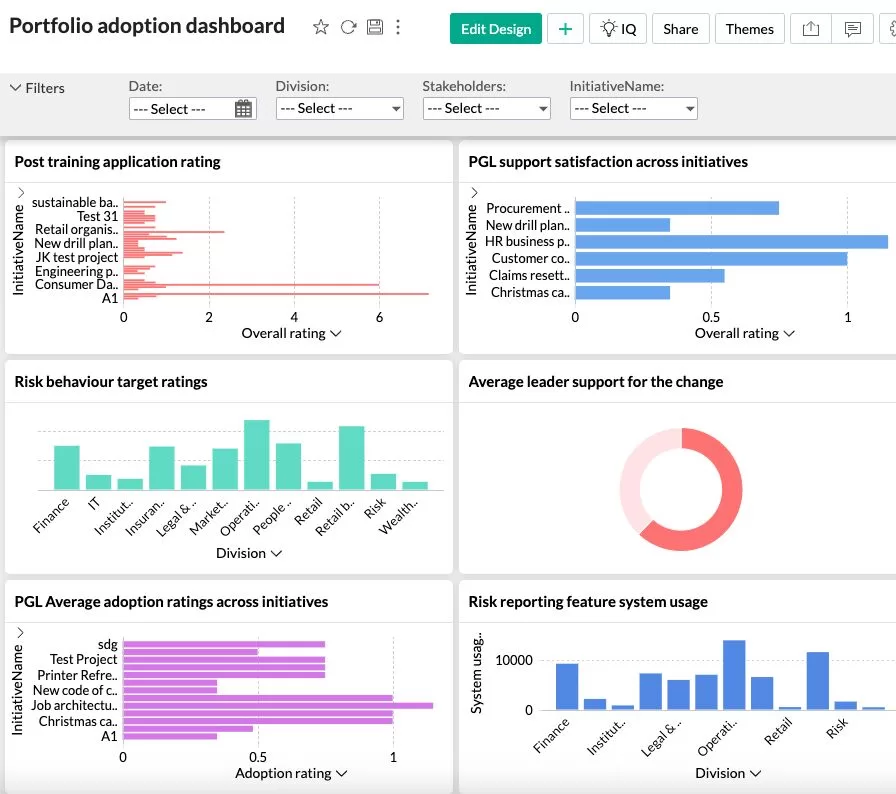
Change adoption dashboard
Now that you have determined exactly what you want to measure to drive adoption, you may want to create a dashboard. Check out our article on ‘Designing a Change Adoption Dashboard’.
What Is a Change Adoption Dashboard?
It’s a visual tool combining key adoption metrics, trends, and warnings into a single pane of glass, allowing leaders and change agents to monitor progress in real time.
Typical Dashboard Widgets
-
System usage and feature adoption rates
-
Compliance audit and incident trend graphs
-
Employee engagement and morale indexes
-
Leadership effectiveness scores
-
Micro-behaviour performance indicators
-
Alerts for underperforming areas or rising risks
To read more about measuring change check out our articles here.
Change adoption is the ultimate goal of any change initiative, and effective measurement of adoption metrics is key to integrating change into daily lives and achieving a product’s success. By understanding the dynamics of change adoption and the user journey, selecting the right metrics, and implementing them effectively, change practitioners and product managers can navigate the complexities of change and drive meaningful outcomes for their organizations. Remember, adoption is not a destination but a journey, and with the right metrics and strategies in place, sustainable change is within reach.
To find out more about leveraging a digital platform to create a change adoption dashboard click the below to chat to us.
Change management is an intricate dance between vision, strategy, execution, and perhaps most importantly, adoption. The ultimate goal of any change initiative is not merely to implement new systems, processes, or regulations, but rather to embed these changes into the very fabric of the organization, ensuring widespread adoption and long-term sustainability.
However, achieving full adoption is no small feat. Many change initiatives falter along the way, failing to garner the buy-in and commitment necessary for success. Even when adoption is initially achieved, sustaining it over time presents its own set of challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the most important adoption metrics in change management?
The most important metrics vary by initiative but generally include user engagement, behavioural compliance, feature usage, retention rates, and customer satisfaction.
2. How do you measure user adoption of a new system?
Measure system feature usage frequency, process efficiency improvements, support ticket trends, and user satisfaction surveys.
3. How do you track behaviour change in employees?
Use a combination of observational data, manager assessments, compliance audits, and micro-behaviour tracking such as task completion accuracy.
4. How many change adoption metrics should organizations track?
Focus on 8 to 15 core metrics aligned with your primary objectives to avoid overwhelm and maximize impact.
5. What tools can I use to build a change adoption dashboard?
Platforms like The Change Compass provide integrated solutions for automated data collection, visualization, and alerting tailored to adoption measurement.
6. How does continuous monitoring improve change adoption?
It allows early detection of issues and timely interventions, preventing small problems from undermining overall adoption success.