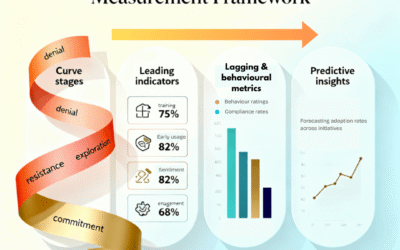
Change measurement translates organisational impact into quantifiable data through surveys, analytics dashboards, and AI-powered tools. Organisations that measure change readiness and adoption rates are 78% more likely to meet project objectives. This guide covers six project-level methods, seven business-level measures, and three enterprise-level frameworks across the Plan-Execute-Realise lifecycle.
A lot of change practitioners are extremely comfortable with saying that change management is about attitudes, behaviours, and feelings and therefore we cannot measure them. This metaphor that change management is ‘soft’ extends into areas such as leadership and employee engagement whereby it may not be easy to measure and track things. However, is it really that because something is harder to measure and less black and white that there is less merit in measuring these?
“If you can’t measure it you can’t improve it” Peter Drucker
The ‘why’ behind a lot of industry change in our day and age comes from the fact that data is now dominating our world. Data is a central part of everything that is changing in our world. Since we are now more reliant on the internet for information, the data that can be collected through our digital interactions around our lives are now driving change. Home assistant Alexa from Amazon can recognize our voices and tell us what we want to know. We can be identified through street cameras. Our Google usage leads to better-targeted advertisements and product promotions. Our Facebook usage leads to a deep understanding of our preferences and lifestyles, and therefore we become targetted by advertisements for what we may find value in (according to Facebook data and algorithms).
So if our world is surrounded by data, why are we not measuring it in managing change? To answer this question let’s look at what we are or are not measuring.
These are some of the common ways in which change is often measured in projects:
Project methods intro
1. Change readiness surveys – What do readiness surveys actually measure?
Change readiness surveys are 5-10 question pulse assessments (Likert + open text) sent via SurveyMonkey/Microsoft Forms at pre-launch, mid-execution, and post-launch. They benchmark stakeholder preparedness, with 92% accuracy when combined with behavioural observations. Top organisations survey quarterly.
Change readiness surveys are usually online surveys sent by a project owner to understand how stakeholder groups are feeling about the change at different points in time throughout the project. It can be in the form on a Likert scale or free text. Most results are summarized into a quantitative scale of the degree in which the group is ready for change. A simple SurveyMonkey could be set up to measure stakeholder readiness for change. ChangeTracking (now part of Accenture) is a comprehensive online tool that measures the change journey and readiness of stakeholder groups throughout the initiative.
2. Training evaluation surveys – How do you prove training ROI?
These evaluations are normally based on participant satisfaction across various categories such as content, instructor effectiveness, usefulness, etc. In a face-to-face training format, these surveys are normally paper-based so as to increase the completion rate. For online or virtual training, ratings may be completed by the user at the conclusion or after the session.
3. Communications metrics – Which comms metrics matter most?
One way in which communications may be measured is the ‘hit rate’ or the number of users/audience that views the article/material/page. This may be easily tracked using Google Analytics that not only tracks number of views per page but also viewership by the time of day/week as well as audience demographic information as such gender and geographical locations.
4. Employee sentiments/culture surveys – What reveals change resistance early?
There are some organizations that measure employee sentiments or culture over the year and often there are questions that are linked to change. These surveys tend to be short and based on a Likert scale with less open-ended questions for qualitative feedback. Since these surveys are often sent across the entire organization they are a ‘catch-all’ yardstick and may not be specific to particular initiatives.
5. Change heatmaps – When do heatmaps fail (and what works better)?
Some organizations devise change heatmaps on excel spreadsheets to try and map out the extent to which different business units are impacted by change. This artifact speaks to the amount of change and often leads to discussions concerning the capacity that the business has to ‘handle/digest’ change. The problem with most heatmaps is that they are usually categorized and rated by the creator of the artifact (or a limited number of people making judgments), and therefore subject to bias. Data that is based on 1 person’s opinions also tend not to have as much weight in a decision-making forum.
6. Change benefit tracking – How do you track post-launch ROI?
In addition to typical change management measures, there are various initiatives-specific measures that focus on the actual outcome and benefit of the change with the goal of determining to what extent the change has taken place. Some example of this includes:
-
System usage rates
-
Cost reduction
-
Revenue increase
-
Transaction speed
-
Process efficiency
-
Speed of decision making
-
Customer satisfaction rate
-
Employee productivity rate
-
Incidents of process violation
Non-initiative based change management measures
There are two other measures that are used within an organizational vs. initiative-specific context, change leadership assessment and change maturity assessment. In the next section, we will discuss these two areas.
Change leadership assessment
David Miller from Changefirst wrote about 3 types of change leaders.:
1. The sponsor whose role is to drive the initiative to success from the beginning to the end. This involves possessing competencies in rallying and motivating people, building a strong network of sponsors and communicating clearly to various stakeholder groups.
2. The influencer whose role is to leverage their network and influence to market and garner the traction required to make the initiative successful. Four types of influencers as identified by Changefirst includes:
a) Advocates who are great at promoting and advocating the benefits of the change
b) Connectors who are able to link and leverage people across a part of the organization to support the change
c) Controllers who have control over access to information and people and these could include administrators and operations staff
d) Experts who are viewed by others in the organization as being technically credible
3. The change agent is someone who is tasked with supporting the overall change in various ways, including any promotional activities, gaging different parts of the organization on the change and be able to influence, up, down and sideways across the organization to drive a successful change outcome.
Whilst there isn’t one industry standard tool for assessing change leadership competencies and capabilities. There are various change leadership assessment tools offered by Changefirst as well as other various smaller consulting firms. One of the most comprehensive change leadership assessment tools is by ChangeTracking is the Change Capacity Assessment which is a self-assessment with the broad categories being Goal Attainment, Flexibility, Decision Making, and Relationship Building.
Some of the key competencies critical in change leadership have been called out by Pagon & Banutal (2008), and include:
-
Goal attainment
-
Assessing organizational culture and climate
-
Change implementation
-
Motivating and influencing others
-
Adaptability
-
Stakeholder management
-
Collaboration
-
Build organizational capacity and capability for change
-
Maneuvering around organizational politics
Change maturity assessment
Organisations are increasingly realising that managing change initiative by initiative is no longer going to cut it as it does not enable organizational learning and growth. Initiatives come and go and those who rely on contractor change managers often find that their ability to manage change as an organization does not mature much across initiatives.
Change maturity assessment is focused on building change capability across the organization across different dimensions, whether it be project change management or change leadership. The goal of conducting a change maturity assessment is to identify areas in which there may be a capability gap and therefore enable structured planning to close this gap.
There are 2 major change maturity assessment models available in the market. The first is by Prosci and the second is by the Change Management Institute. To read more about change maturity assessment read out article A New Guide for Improving Change Management Maturity, where we outline how to improve change maturity throughout different business units across the organization.
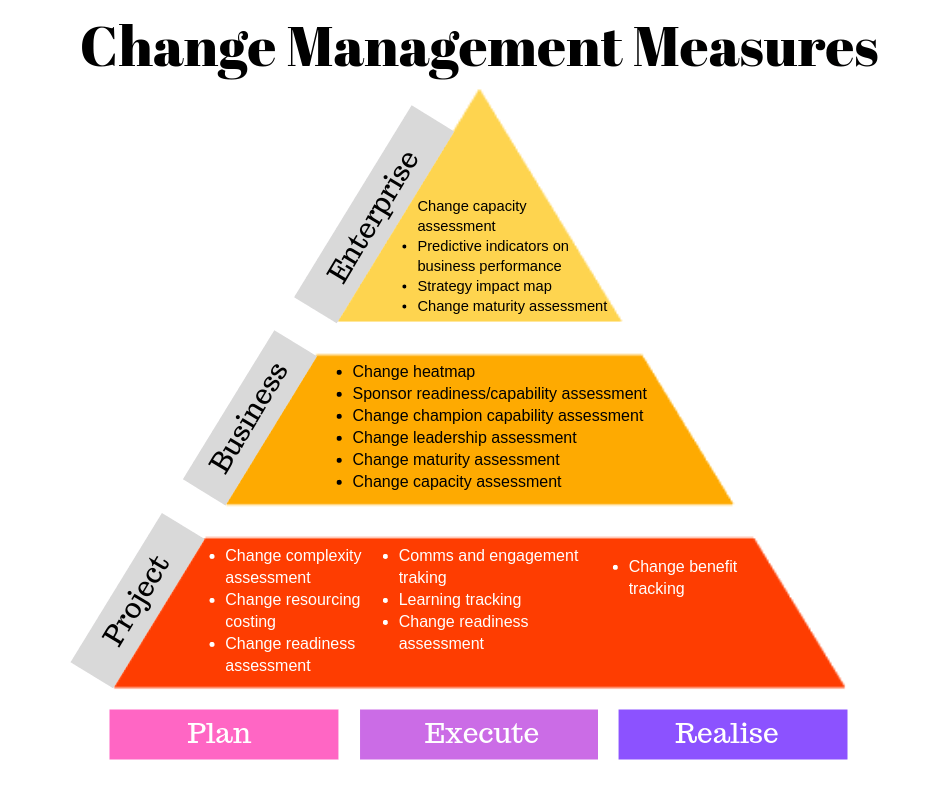
A comprehensive model of Change Management Measures
In this diagram various change management measures are represented along two axes, one being the different phases of the initiative lifecycle, and the other being different organizational levels of project, business and enterprise in which change management measures fall into.
Project level measures
‘Plan’ phase
In this phase of the project, the team is discovering and scoping what the project involves and what the change is. As a result, the details are not known clearly at the commencement of the phase. Later in the phase the scope becomes much clearer and the team starts to plan what activities are required to implement the change.
-
The change complexity assessment evaluates how complex the project is. It looks at how many people could be impacted, what the size of the impact could be, how many business units are impacted, whether multiple systems and processes are impacted, etc.
-
Change resourcing costing. At the planning phase of the project cost required for the change management stream of the work is required. This includes such as any contractors, communication campaigns, learning cost, travel, and administration cost, just to name a few.
-
Change readiness assessment is usually conducted prior to the change and during the change. Usually, the same set of questions is asked of various stakeholder groups to assess their readiness for change.
‘Execute’ phase
The execute phase is one of the most critical parts of the project. Activities are in full flight and the project is busy iterating and re-iterating changes to ensure successful execution to achieve project goals.
-
Communication and engagement tracking. Effective engagement of stakeholders in the change is absolutely critical. Stakeholder interviews, surveys, communication readership rates are all ways in which engagement may be tracked.
-
Learning tracking. Measuring learning is critical since it tracks to what extent the new competencies and skills have been acquired through learning interventions. Typical measurements include course tests or quizzes in addition to course evaluations. On the job performance may also be used to track learning outcomes and to what extent learning has been applied in the work setting.
-
Change readiness assessment continues to be critical to track during the execution phase of the project
‘Realise’ phase
In this phase of the project the change has ‘gone live’ and most project activities have been completed. It is anticipated in this phase that the ‘change’ occurs and that the benefits can then be tracked and measured.
-
Change benefit tracking measures and tracks the extent to which the targeted benefits and outcomes have been achieved. Some of these measures may be ‘hard’ quantitative measures whilst others may be ‘soft’ measures that are more behavioural.
Business level measures
Business level measures are those that measure to what extent the business has the right ability, capacity, and readiness for the change.
-
Change heatmaps can help to visualize which part of the business is most impacted by 1 project or multiple projects. The power of the change heatmap is in visualizing which part of the business is the most impacted, and to compare the relative impacts across businesses. As the number of change initiatives increase so would the complexity of the change. When facing this situation organisations need to graduate from relying on excel spreadsheets to using more sophisticated data visualization tools to aid data-based decision making. To read more about change heatmaps and why this is not the only way to understand business change impact, go to The Death of the Change Heatmap.
-
Sponsor readiness/capability assessment can be a critical tool to help identify any capability gaps in the sponsor so that effort may be taken to support the sponsor. A strong and effective sponsor can make or break a change initiative. Early engagement and support of the sponsor are critical. Both Prosci, as well as Changefirst, have sponsor competency assessment offerings.
-
Change champion capability assessment. Change champion or change agent are critical ‘nodes’ in which to drive and support change within the organizational network. A lot of change champions are appointed only for one particular initiative. Having a business-focus change champion network means that their capability can be developed over time, and they can support multiple initiatives and not just one. Assessing and supporting change champion capability would also directly translate to better change outcomes.
-
Change leadership and change maturity assessment – refer to the previous section
-
Change capacity assessment.
In an environment where there is significant change happening concurrently, careful planning and sequencing of change in balance with existing capacity are critical. There are several aspects of change capacity that should be called out in the measurement process:
- Different parts of the business can have different capacity for change. Those parts of the business with better change capability, and perhaps with better change leadership, are often able to receive and digest more changes than other businesses that do not possess the same level of capability.
- Some businesses are much more time-sensitive and therefore their change capacity needs to be measured with more granularity. For example, call centre staff capacity is often measured in terms of minutes. Therefore, to effectively plan for their change capacity, the impacts of change needs to be quantified and articulated in a precise, time-bound context so that effective resourcing can be planned in advance.
- The change tolerance or change saturation level for business needs careful measurement in combination with operational feedback to determine. For example, it could be that last month a part of the business experienced significant change impact across several initiatives happening at the same time. The operational indicators were that there was some impact on customer satisfaction, productivity, and there were negative sentiments reported by staff that there was too much change to handle. This could mean that the change tolerance level may have been exceeded. With the right measurement of change impact levels for that part of the business, next time this level of change is seen, previous lessons may be utilized to plan for this volume of change. Utilise measurement and data visualization tools such as the Change Compass to track change capacity.
Enterprise level change measures
At an enterprise level, many of the business unit level measures are still applicable. However, the focus is comparing across different business units to sense-make what each part of the business is going through and if the overall picture is aligned with the intentions and the strategic direction of the organization. For example, typical questions include:
-
Is it surprising that one part of the business is undergoing significant change whilst another is not?
-
Is there a reason that one business unit is focused on a few very large changes whilst for other business units there is a larger set of changes each with smaller impacts?
-
Is the overall pace of change optimum according to strategic intent? Does it need to speed up or slow down?
-
What is the process to govern, report and make decisions on enterprise level change, prioritization, sequencing and benefit realization?
-
Is there one business unit that is able to manage change more effectively, faster with greater outcomes? How can other business units leverage any internal best practices?
As mentioned in the Change Management Measures diagram, some enterprise level change measures include:
-
Change capacity assessment – Does one business unit’s change capacity limits mean that we are not able to execute on a critical strategy within the allocated time? How do we create more capacity? Ways in which to create more capacity could include more resources such as staff, or initiative funding, more time is given, or more talent to lead initiatives
-
Change maturity assessment – At an enterprise level, the concern is with the overall change maturity of the organization. How do we implement enterprise level interventions to build change maturity through programs, networks, and exchanges, such as:
-
Enterprise change capability programs
-
Enterprise change analytics and measurement tools
-
Enterprise change methodology
-
Enterprise network of change champions
-
-
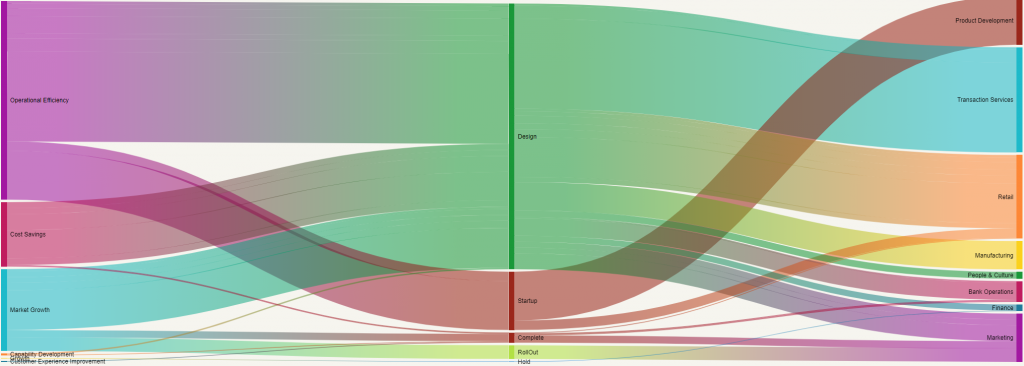
Strategy impact map – Change management need not be focused only on project execution or business unit capability. It can also demonstrate value at an enterprise level by focusing on strategy execution (which by definition is change). The way in which different strategies exert impact on various business units may be visualized to help stakeholder understand which initiatives within which strategic intent impact which business units. To illustrate this please refer to the below diagram which is an example of a strategy impact map. In this diagram, each of the organisation’s strategy is displayed with different initiatives branching out of each strategy. The width of each initiative correlates with the level of impact that the initiative has on the business over a pre-determined period of time. Therefore, the width of each strategy also indicates the overall relative impact on the business.
This data visualization artifact can be valuable for business leaders and strategic planning functions as it depicts visually how the implementation of various strategies is impacting business units. This helps planners to better understand strategy implementation impacts, potential risks and opportunities, and balancing change pace with strategy goals at various points in time.
-
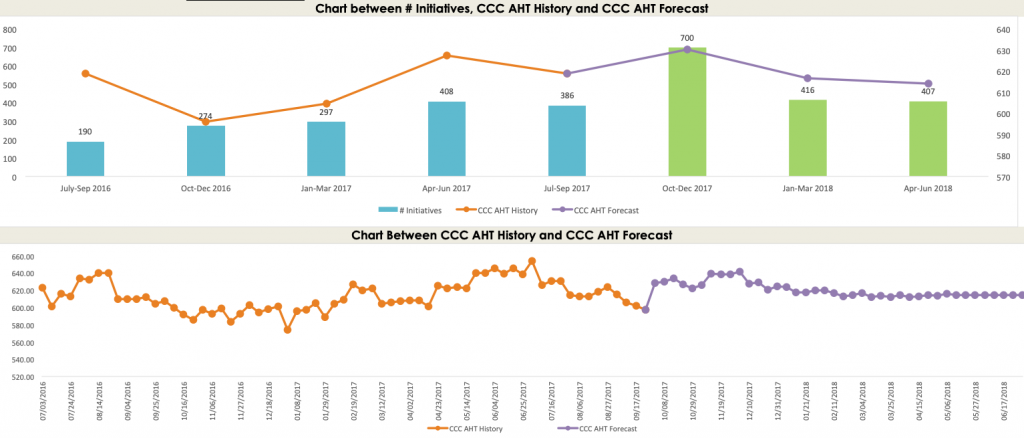
Predictive indicators on business performance – We started this article talking about how data is all around us and we also need to better manage change using data. With quantitative data on change impact, it is possible to ascertain any correlations with operational business indicators such as customer satisfaction, service availability, etc. For those business indicators where there is a significant correlation, it is possible to hence use predictive reporting to forecast performance indicator trends, given planned change impacts.
In the below graph you can see an example of this whereby using historical data it is possible to establish correlations and therefore forecast future impact on business indicators. This example is focused on the customer contact centre (CCC) and key business indicator of average handling time (AHT) is utilized as an illustration.
This type of predictive performance forecasting is extremely valuable for organisations undergoing significant change and would like to understand how change may impact their business performance. By demonstrating the impact on business indicators, this puts the importance of managing change at the front and centre of the decision-making table. At The Change Compass, we are developing this type of measurement and reporting function. This is the frontier for change management – to be established as a key business-driving function (versus a standard back-office function).
Change can be measured and this article has outlined various operational and strategic ways in which change measurement can demonstrate significant value. Most corporate functions cannot exist without data and analytics. For example, Human Resources relies on people and pay data. Marketing cannot function without measurement of channel and campaign effectiveness. For Information Technology, pretty much everything is measured from system usage, to cost, to efficiency. It is time we start utilizing data to better visualize change to better plan and make business decisions.
References:
Miller, David (2011) Successful Change. How to implement change through people. Changefirst Ltd.
Pagon & Banutal (2008) Leadership Competencies for Successful Change Management. Study Report. University of Maribor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the most important change management metrics to track?
Focus on adoption rates, readiness scores, communication engagement, and benefit realisation metrics tailored to project phases and business capacity.
How do you measure change readiness effectively?
Combine pulse surveys with behavioural indicators and sponsor assessments. Balance frequency with depth for actionable insights. Read “Beyond the Survey: A Strategic Lens on Change Readiness Assessment.”
Why replace change heatmaps with other visuals?
Heatmaps introduce subjectivity bias. Timeline charts and capacity dashboards provide clearer decision-making data. See “The Death of the Change Heatmap.”
What role does AI play in change measurement?
AI enables real-time sentiment analysis, predictive capacity planning, and automated risk detection across initiatives. Platforms integrate natural language queries for instant insights.
How many change metrics should organisations track?
Target 8-15 core metrics aligned with strategic objectives across project, business, and enterprise levels to maintain focus and actionability.
What enterprise-level change metrics matter most?
Strategy impact mapping, cross-business capacity analysis, and predictive performance forecasting linking change volume to operational outcomes.